Fig. 2. Cells expressing psMEK1 and ERK KTR sensor enables all-optical cell-based assay for MEK and ERK inhibitors.
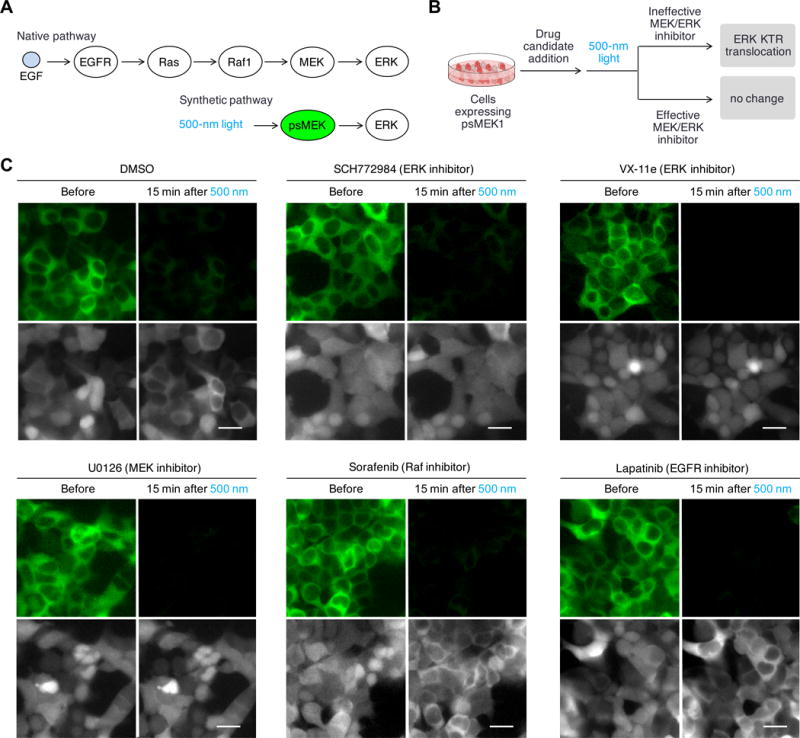
(A) In native pathway, chemical ligands such as EGF activates receptor kinases EGFR, which then activates Ras. Activated Ras binds and activates Raf-1, which leads to MEK activation. In the synthetic pathway, psMEK1 is solely controlled by light and no longer respond to upstream activations. (B) Proposed all-optical cell-based assay for MEK and ERK inhibitors. Cells expressing psMEK1-P2A-ERK KTR-mRuby would be first incubated with drug candidates and then stimulated with light. The distribution of ERK KTR-mRuby2 would be monitored to determine whether light could induce ERK phosphorylation in the presence of the drug. (C) The assay allowed determination of inhibitors specifically targeting MEK and ERK. Upper panels, 1 min of cyan light stimulation at 200-mW/cm2 switched off pdDronpa fluorescence; lower panels, ERK KTR-mRuby2 translocation was monitored. We observed that cells incubated with ERK inhibitor SCH772984 and VX-11e, and MEK inhibitor U0126, did not show ERK KTR-mRuby2 translocation in response to psMEK1 activation, but cells incubated with DMSO or inhibitors against upstream MEK activators Raf1 or EGFR, Sorafenib and Lapatinib, showed ERK KTR. Scale bar, 20 μm.
