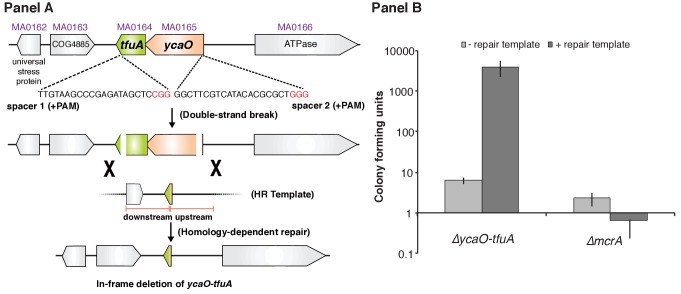
Figure 3. Panel A, Experimental strategy for deletion of the ycaO-tfuA locus in M. acetivorans using a Cas9-mediated genome editing technique.
Co-expression of the Cas9 protein along with a single guide RNA (sgRNA) with a 20 bp target sequence flanked by a 3’ NGG protospacer adjacent motif on the chromosome (PAM; in red) generates double-stranded breaks at the ycaO-tfuA locus. Repair of this break via homologous recombination with an appropriate repair template (HR Template) generates an in-frame deletion on the host chromosome. Panel B, A Cas9-based assay for gene essentiality. Mean transformation efficiencies of plasmids with (dark gray) or without (light gray) an appropriate repair template are shown. The known essential gene mcrA is included as a positive control. The error bars represent one standard deviation of three independent transformations.
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. A PCR-based screen to genotype the ycaO-tfuA locus in Methanosarcina acetivorans.