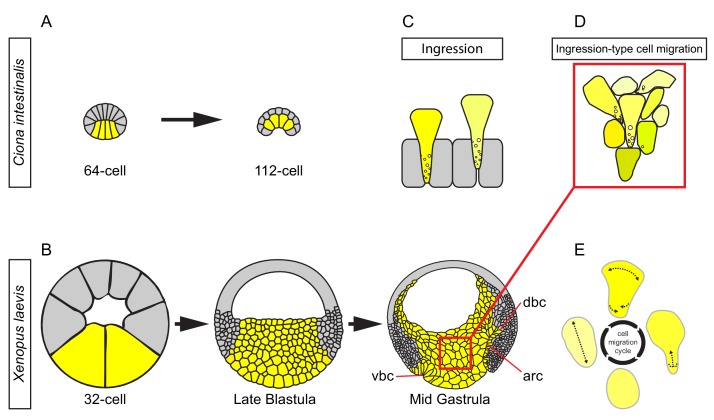
Figure 11. Ingression-type cell migration during X.
laevis vegetal rotation. (A) Endodermal cells (yellow) invaginate in ascidians. Schematic of Ciona intestinalis embryos at 64 and 112 cell stages. (B) Vegetal rotation in amphibians. Schematic of Xenopus laevis embryos at 32 cell, late blastula, and mid-gastrula stages. Endoderm cells of the vegetal endoderm, the suprablastoporal endoderm, and bottle cells are shown in yellow. Inset indicates cells shown in (D). Archenteron (arc), dorsal bottle cells (dbc), and ventral bottle cells (vbc) are indicated. (C) Generalized schematic of epithelial cell ingression shows ingressing cells (yellow) next to non-ingressing cells (grey). Internalized membrane vesicles are shown at the trailing edges. (D) Ingression-type cell migration. Schematic shows endoderm cells undergoing differential amoeboid migration in the vegetal cell mass. (E) Endoderm cells rearrange by cycling through a series of amoeboid migration behaviours (indicated by dashed lines) which include cell body elongation, cell front expansion in tandem with cell rear narrowing which is required for trailing edge retraction.