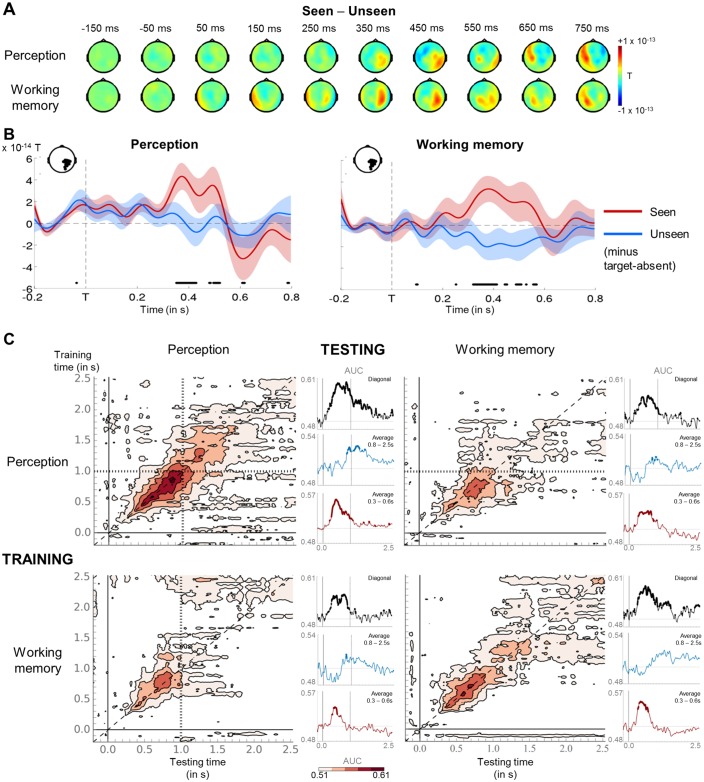
Figure 3. Neural signatures for conscious perception and maintenance in working memory.
(A) Sequence of brain activations (−200–800 ms) evoked by consciously perceiving the target in the perception (top) and working memory (bottom) task. Each topography depicts the difference in amplitude between seen and unseen trials over a 100 ms time window centered on the time points shown (magnetometers only). (B) Average time courses of seen and unseen trials (−200–800 ms) after subtraction of target-absent trials in a group of parietal magnetometers in the perception (left) and working memory (right) task. Shaded area illustrates standard error of the mean (SEM) across subjects. Significant differences between conditions are depicted with a horizontal, black line (Wilcoxon signed-rank test across subjects, uncorrected). For display purposes, data were lowpass-filtered at 8 Hz. T = target onset. (C) Temporal generalization matrices for decoding of visibility category as a function of training and testing task. In each panel, a classifier was trained at every time sample (y-axis) and tested on all other time points (x-axis). The diagonal gray line demarks classifiers trained and tested on the same time sample. Please note the event markers in any panel involving the perception task: Mean reaction time (target-present trials) for the visibility response is indicated as vertical and/or horizontal, dotted lines. Any classifier beyond this point only reflects post-visibility processes. Time courses of diagonal decoding and of classifiers averaged over the P3b time window (300–600 ms) and over the working memory maintenance period (0.8–2.5 s) are shown as black, red, and blue insets. Thick lines indicate significant, above-chance decoding of visibility (Wilcoxon signed-rank test across subjects, uncorrected, two-tailed except for diagonal). For display purposes, data were smoothed using a moving average with a window of eight samples. AUC = area under the curve.