Figure 5. Structural comparison of HLA-A2 bound RQI phosphopeptide in modified and unmodified states.
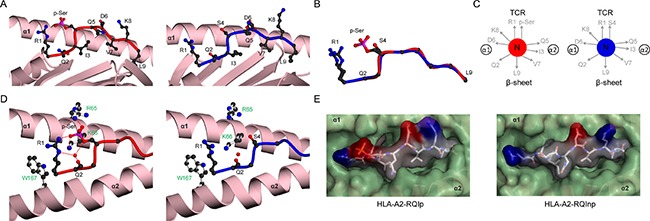
(A) HLA-A2 bound structures of RQIp (left, red) and RQInp (right, blue), derived from adenosine monophosphate deaminase. The α1-α2 antigen binding platform is shown in ribbon representation (pink), with α2 helix residues 137-166 omitted for clarity. (B) Superposition of the RQI main chain structures for phosphorylated (red) and non-phosphorylated (blue) peptides, including the R1 and S4/p-Ser side-chains. (C) Side-chain orientation for phosphorylated (left, red) and non-phosphorylated (right, blue) RQI peptides, as viewed along the long axis of the peptide from its N-terminus. (D) Interactions of position 4 side chains for phosphorylated (left, red main chain) and non-phosphorylated (right, blue main chain) peptides with HLA-A2 α1-α2 helices (pink). Hydrogen bonds are indicated by red dashed lines; red spheres represent water molecules; for clarity the underlying β-sheet is omitted. HLA-A2 side chains are shown as white sticks and labelled green. (E) Molecular surface of phosphorylated (left) and non-phosphorylated (right) RQI peptides, as viewed from the perspective of the TCR. Color scheme as in Figure 4D.
