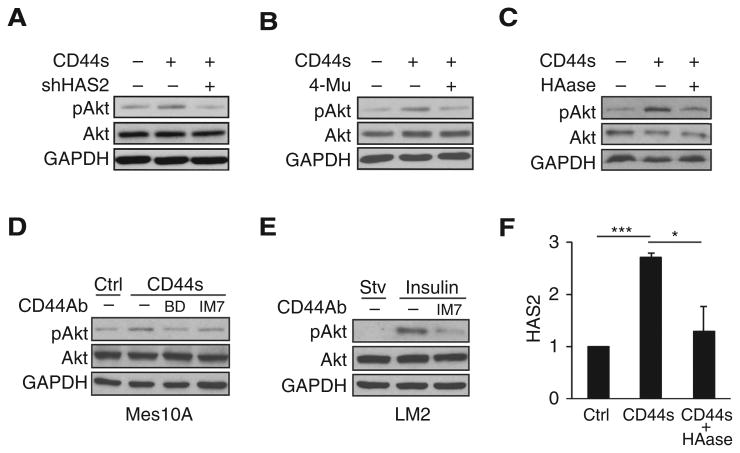
Figure 5.
CD44-mediated Akt activation is dependent on HAS2/HA. A–C, Immunoblot analysis of pAkt levels showing that knockdown of HAS2 (A), treatment with HAS2 inhibitor 4-Mu (0.4 mmol/L; B), or treatment with HAase (35 μg/mL; C) abolished Akt activation in CD44s-overexpressing Mes10A cells. Cells were stimulated with insulin 10 μg/mL for 30 minutes. D, Immunoblot analysis showing that addition of CD44 antibodies abolishes CD44s-promoted Akt activation in CD44s-overexpressing Mes10A cells. BD clone 515 and IM7 antibodies were added at 1 μg/mL concentration in starvation media overnight. Cells were then washed with PBS and stimulated with insulin (10 μg/mL; 30 minutes). E, Immunoblot analysis showing that the CD44 antibody IM7 blocks Akt activation in LM2 cells. LM2 cells were starved overnight and then treated with IM7 antibody (10 μg/mL) for 3 hours, followed by insulin stimulation (10 μg/mL; 30 minutes). F, qRT-PCR analysis of HAS2 in control, CD44s-overexpressing, and HA-depleted CD44s-overexpressing Mes10A cells. Treatment of CD44s-overexpressing Mes10A cells with HAase (90 μg/mL) for 8 hours reduced CD44s-mediated HAS2 transcription. Error bars, SD; n = 3. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001.