Fig. 1.
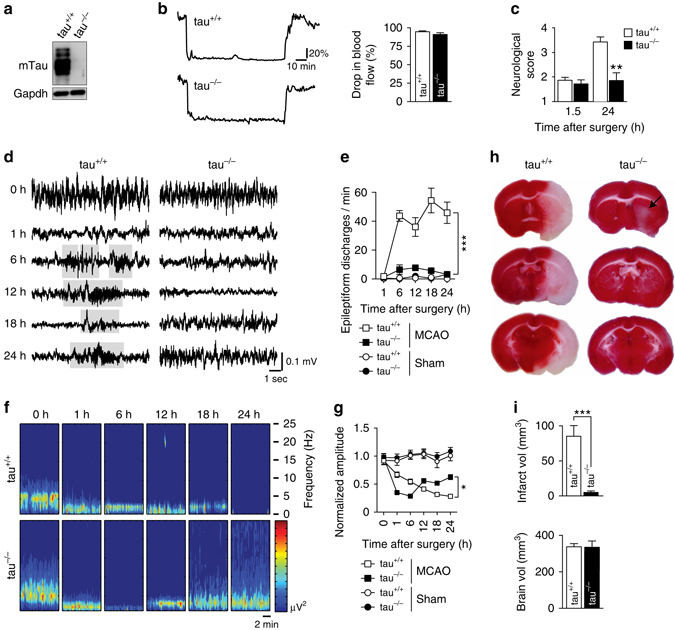
Tau−/− mice are protected from neurological deficits, aberrant hyperexcitation and extensive brain damage after transient MCAO. a Western blotting for murine tau (mTau) in brain extracts from tau+/+ and tau−/− mice. GAPDH confirmed equal loading. b Ischemic stroke was induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) for 1.5 h with subsequent reperfusion. Drop in blood flow in the MCA was the same in tau−/− and tau+/+ mice during MCAO, as determined by laser Doppler flowmetry (not significant; N = 12; Student’s t-test). Unit, % of baseline flow. c Neurological scoring (with higher numbers indicating more severe impairments) revealed similar deficits directly after MCAO in tau−/− and tau+/+ mice. Only tau+/+ mice showed a worsening of deficits at 24 h (**P < 0.01; N = 12; 2-way ANOVA (Sidak post hoc)). d Representative electroencephalography (EEG) recordings in tau−/− and tau+/+ mice at baseline (0 h) and indicated times after transient MCAO. Suppressed EEG signals recovered after 12 h following MCAO in tau−/− mice, while tau+/+ mice presented with epileptiform discharges (gray boxed) after 6 h. e Quantification revealed persistently high numbers of epileptiform discharges 6 h after transient MCAO (***p < 0.001 vs. tau−/− MCAO; N = 5; two-way ANOVA (Bonferroni post hoc)). A small increase in epileptiform spike trains was transient in tau−/− mice, and reached levels of sham operated tau−/− and tau+/+ mice 24 h after transient MCAO. f EEG frequency power spectrum (0–25 Hz) tau+/+ and tau−/− mice at baseline (0 h) indicated times following transient MCAO, with recovery only in tau−/− animals. g Quantification of EEG recordings showed a progressive amplitude decline in tau+/+ mice that partial recovered tau−/− animals (*p < 0.05; N = 5; two-way ANOVA (Bonferroni post hoc)). h TTC-stained serial brain sections of tau+/+ and tau−/− mice 24 h after MCAO (viable tissue stains red). Note the large infarcted area (white) in tau+/+, while only minimal brain damage was present in tau−/− mice (arrow). i Volumetric quantification of infarct and brain volumes in tau+/+ and tau−/− mice 24 h after transient MCAO (***p < 0.001; N = 12; Student’s t-test). All error bars are s.e.m
