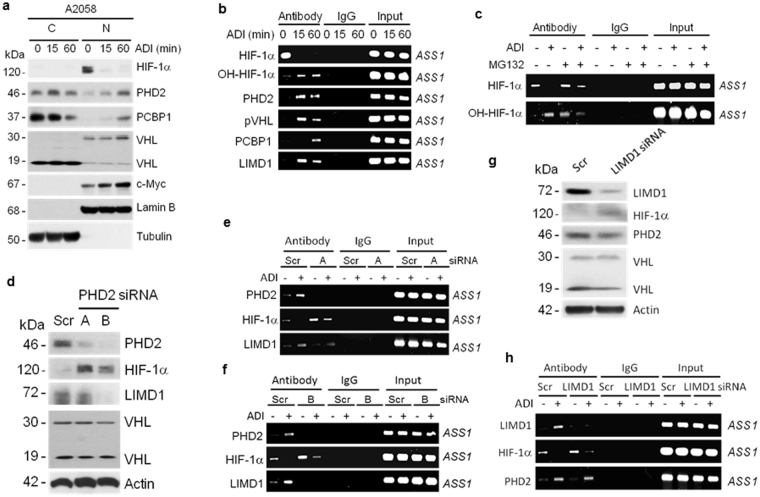
Figure 2.
ADI induces HIF-1α degradation at the ASS1 promoter and mobilization of PHD2-inteacting proteins to the promoter. (a) Western blots show the turnover of HIF-1α and its degrading proteins in response to ADI treatment. A2058 cells were treated with ADI for the time intervals as indicated. Cells were fractionated into cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) fractions. Protein levels were determined by Western blotting using α-tubulin as cytoplasmic and lamin B and c-Myc as nuclear controls, respectively. (b) ChIP assay for the ASS1 promoter associations of various proteins in A2058 cells treated with ADI for the time points as indicated. Antibodies used in ChIP are shown on the left, where ASS1 promoter sequence was determined by polymerase chain reaction by agarose gel electrophoresis and is shown on the right. Note that HIF-1α degradation and hydroxylated HIF-1α formation were induced by ADI. Promoter recruitments of PHD2, pVHL, PCBP1 and LIMD1 were induced by ADI. (c) ADI-induced HIF-1α degradation at the ASS1 promoter is partially suppressed by MG132. (d) Effects of PHD2 knockdown using two siRNA (designated as A and B) on the expression of HIF-1α and other proteins as indicated. (e,f), ChIP assays on the effects of PHD2 knockdown by PHD2 siRNA (A and B) on the ASS1 promoter associations of HIF-1α and LIMD1. (g) Effects of LIMD1 knockdown on the expression of HIF-1α and its associated proteins. (h) Effects of LIMD1 knockdown on the associations of HIF-1α and PHD2 to the ASS1 promoter. Scr, scrambled siRNA.