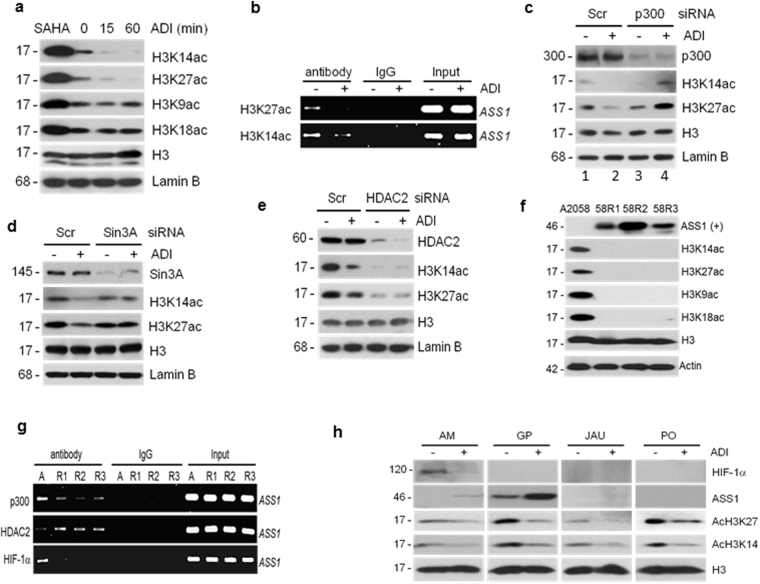
Figure 5.
Effects of histone H3 deacetylation by ADI. (a) A2058 cells were treated with ADI for the time intervals as indicated, or with SAHA (20 μM for 1 hr as positive control), and lamin B expression (as control for sample loading). Acetylation status of various modified histones H3 were determined. (b) Reduction of ASS1-promoter associations of H3K27ac and H3K14ac by ADI (0.5 μg/ml, 15 min.). (c to e), Effects of p300, Sin3A, and HDAC2 knockdown by siRNAs, respectively, on the expression levels of H3K14ac and H3K27ac in A2058 cells treated with or without ADI. (f) Western blotting analyses of H3K14ac, H3K27ac, H3K9ac, and H3K18ac expression in A2058 and ADI-resistant (ADIR variants, 58R1 to 58R3). (g) ChIP assay of promoter-associations of p300, HDAC2, and HIF-1α in A2058 and ADIR cells (R1 to R3). (h) Western blotting analyses of HIF-1α, ASS1, H3K14ac, H3K27ac, and H3 expression in 4 matched pairs of primary cell lines derived from melanoma patients before (−) and after failed (+) by ADI treatments.