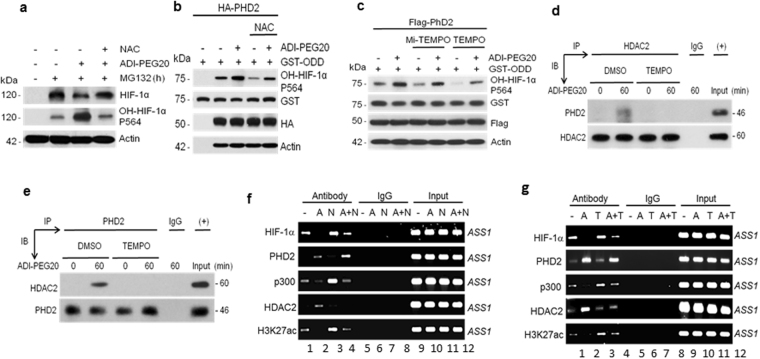
Figure 6.
Effects of ROS on ADI-induced HIF-1α degradation. (a) ADI-induced HF-1α degradation is inhibited by antioxidant, NAC. A2058 cells were treated with 10 μM MG-132 in the absence or presence of ADI or NAC (1 mM) for 4-h. Expression levels of HIF-1α, hydroxylated HIF-1α, and actin were determined by Western blotting. (b) The antioxidant NAC suppresses ADI-induced PHD2 enzymatic activity. A2058 cells were transfected with recombinant encoding HA-PHD2. Cells were treated with NAC or ADI as indicated for 1 hr. PHD2 enzymatic activity was measured using GST-ODDD (100 ng) as a substrate and production of HO-HIF-1α (p564). (c) Similar to those described in (b) was performed using anti-oxidants Mito-TEMPO (40 μM) and TEMPO (100 μM) for 1 hr. (d,e) Inhibitions of HDAC2 and PHD2 interaction by TEMPO in reciprocal co-IP assays. (f,g), Effects of antioxidants NAC (N, 1 mM) or TEMPO (T, 100 μM)) on ADI (A)-induced ASS1 promoter association of HIF-1α, PHD2, p300, HDAC2 and H3K27ac in A2058 cells treated with or without ADI (A, 0.5 μg/ml, 1 hr) as determined by ChIP assay.