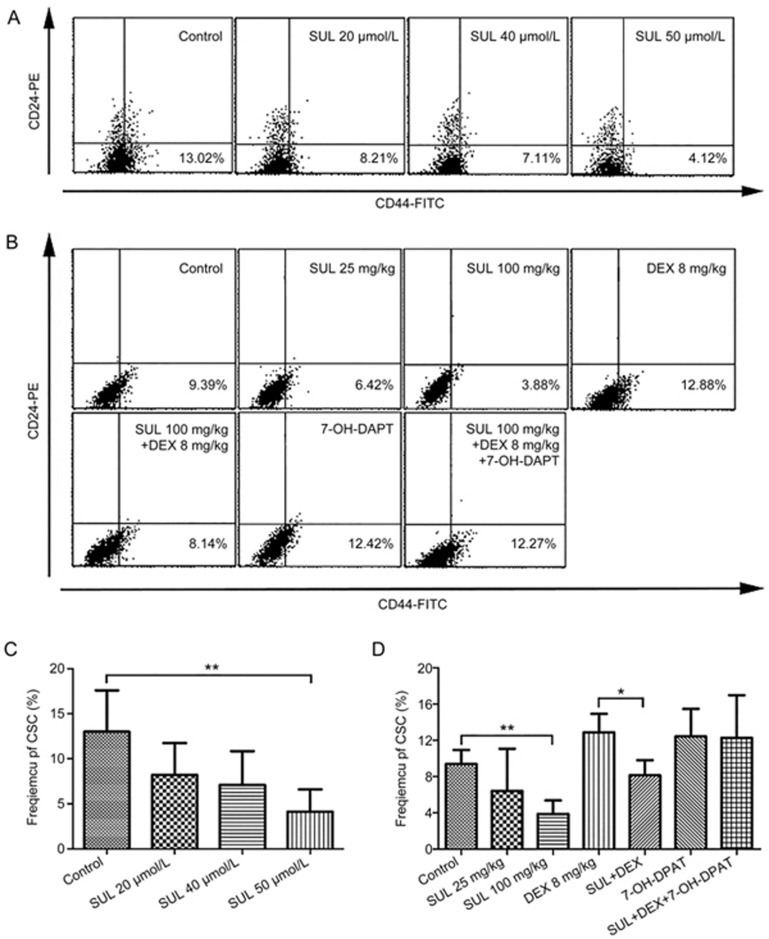
Figure 4.
SUL reduced the proportion of CSCs in vitro (A and C) and in vivo (B and D). In the in vitro analysis, MCF-7/Adr cells were cultured in the presence of DMSO (1%) and different concentrations of SUL (20, 40, 50 μmol/L) for 48 h before staining with anti-CD44-FITC and anti-CD24-PE. CSCs, defined as CD44+/CD24− cells, were measured on a FACScan flow cytometer. (A) Representative flow cytometer analysis of the SUL-induced reduction of CSC frequency. (C) SUL significantly reduced the proportion of CSCs in a dose-dependent manner. In the in vivo analyses, tumor tissues from different treatment groups were minced, digested and incubated at 37 °C for 4–6 h before staining with anti-CD44-FITC and anti-CD24-PE. CSCs (CD44+/CD24− cells) were analyzed on a FACScan flow cytometer. (B) Representative flow cytometer analysis of the changes of CSC frequency. (D) The CSC proportion was remarkably reduced in the SUL monotherapy group, but it increased in the DEX monotherapy group. When DEX was administered in combination with SUL, the proportion of CSCs was significantly reduced, and this effect could be reversed by 7-OH-DPAT. All data are presented as the mean±SD (n=4). SUL, sulpiride; DEX, dexamethasone; *P<0.05, **P<0.01.