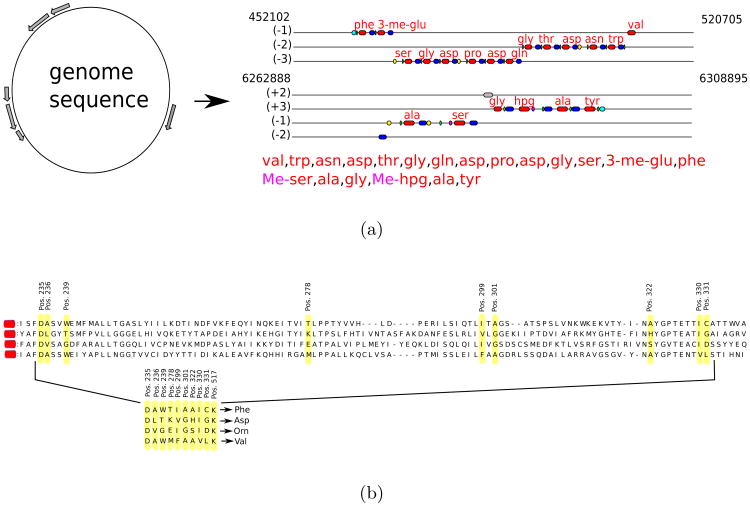
Figure 2.
(a) Pipeline for predicting NRPs based on NRPS analysis (e.g. NRPSpredictor2 [40]). Adenylation domains are shown in red, condensation domains shown in blue, peptidyl carrier protein domains in green, methylation domains in yellow, and thioester domains in purple. (b) Extracting signature sequences (non-ribosomal code) from adenylation domains. The non-ribosomal code postulates that certain amino acids (shown in yellow) in each adenylation domains define a single amino acid in the NRP loaded by this domain. Four shown adenylation domains define 10-aa long signatures DAWTIAAICK, DLTKVGHIGK, DVGEIGSIDK, and DAWMFAAVLK corresponding to amino acids Phe, Asp, Orn, and Val, respectively. The shown 10-aa long signatures is a simplified representation of teh non-ribosomal code, e.g., NRPSpredictor2 uses longer signatures to accurately predict amino acids for each adenylation domain. Only a short segment of the adenylation domains (amino acids 234-337) is shown.