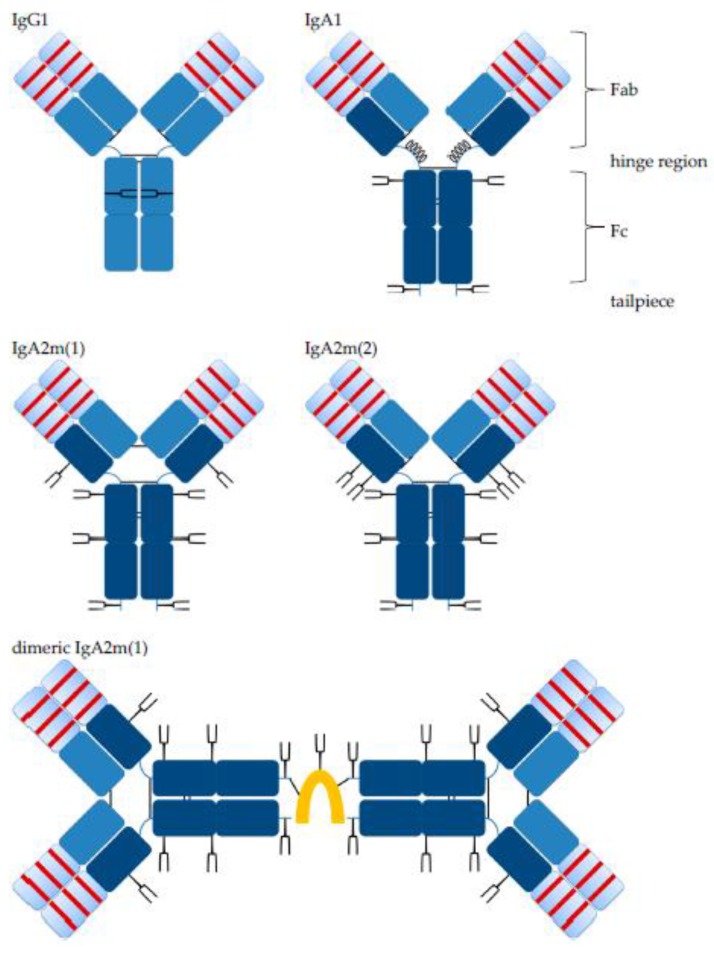
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of IgG1 and IgA antibodies. IgG Cγ and common Cκ light chain domains (both blue) and IgA Cα domains (dark blue) are indicated. Variable domains (light blue) including complementary-determining regions (CDRs, red bars) of heavy and light chains are indicated. N-glycosylation sites (Y) with their different orientation towards the inside or outside of the molecules are indicated for IgG or IgA, respectively. Antibodies might possess N-glycosylation sites within their variable domain, which is not shown here. The tailpiece for IgA antibodies is shown, which is not present for IgG antibodies. Inter-chain disulfide bonds (black lines) of heavy and light chains are indicated and differ between isotypes and allotypes. In contrast to IgA2, in the extended hinge region of IgA1, O-glycosylation sites (0) are present. IgA2m(1) forms disulfide bonds between the two light chains. Dimeric IgA2m(1) include inter-chain disulfide bonds between the J chain (orange) and two IgA monomer units. The J chain stabilizes IgA dimers, but other interactions between IgA monomer units can result in the formation of dimers lacking the J chain. Adopted from Woof and Burton [18].