Figure 1.
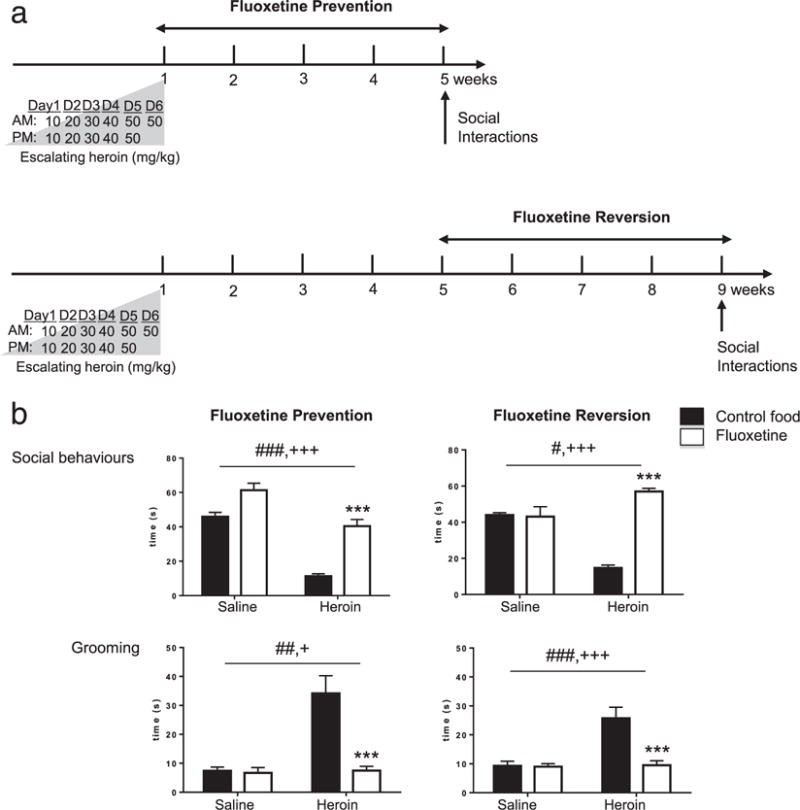
Chronic FLX treatment can both prevent and reverse low sociability in heroin abstinent mice. (a) Timeline for ‘Fluoxetine Prevention’ (upper panel) and ‘Fluoxetine Reversion’ (lower panel) experiments. Following heroin treatment, mice were maintained drug-free to experience spontaneous withdrawal for 4 weeks in prevention or 8 weeks in reversion experiments, followed by behavioral testing (Social Interactions). Mice were fed FLX-supplemented pellets (10 mg/kg/24 hours) during weeks 2 to 5 or weeks 5 to 8, in prevention or reversion experiments, respectively. (b) Social Interactions in ‘Fluoxetine Prevention’ (left panel) and ‘Fluoxetine Reversion’ (right panel) experiments. Consistent with our previous findings, heroin abstinence reduced social behaviors and potentiated grooming. Both of these deficits were prevented (left panel) and reversed (right panel) by 4 weeks of per os FLX treatment. Data represented as mean ± SEM. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, ANOVA, main effect of heroin. +P < 0.05, +++P < 0.001, ANOVA main effect of FLX. ***P < 0.001, post hoc FLX effect in heroin-FLX food mice as compared with heroin-control food mice
