Figure 10.
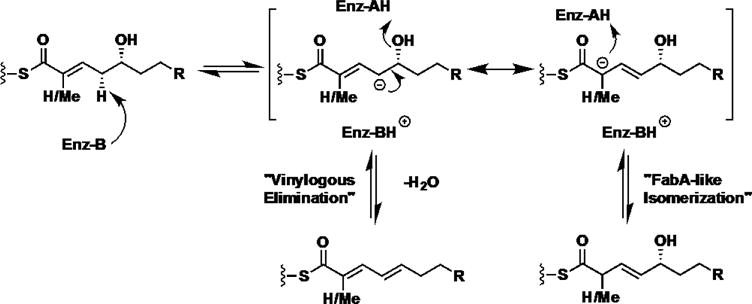
FabA-isomerization mechanism and proposed mechanism of vinylogous dehydration by curacin dehydratases J and H. The two events share a common intermediary vinylogous enolate and only differ only in the final re-protonation or elimination. Site-directed mutagenesis of the catalytic dyad indicates that both the canonical histidine and aspartic residues are the general base and acid, respectively. FabA (Escherichia coli β-hydroxydecanoyl thiol ester dehydrase) catalyzes elimination and bond isomerization in fatty acid biosynthesis.
