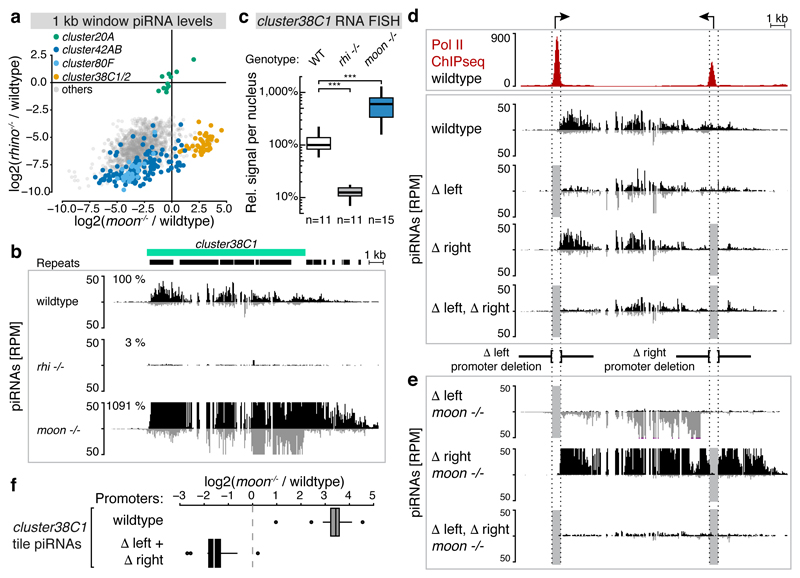
Figure 4. Endogenous piRNA cluster promoters bypass Moonshiner-dependent transcription initiation.
a, Fold changes (log2) of piRNAs mapping uniquely to Rhino-dependent genomic 1kb tiles in rhino versus moonshiner mutants (relative to wildtype). Tiles from major piRNA clusters are colored (cluster20A tiles serve as Rhino-independent control group). b, Genome browser panel showing cluster38C1 piRNA levels from ovaries with indicated genotype. c, Quantification of cluster38C1 RNA FISH signal in germline nuclei relative to that of cluster20A (***: p value < 0.0001; Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon tests; boxplots as in Fig. 3c). d, Pol II occupancy and piRNA levels at cluster38C1 in ovaries with indicated genotypes. Δleft and Δright indicate cluster38C1 promoter deletions (light grey boxes). e, as d, but from moonshiner mutant ovaries. f, Boxplot (defined as in Fig. 3c) displaying log2(fold changes) in cluster38C1 piRNA levels (n=12 1kb windows) in moonshiner mutant compared to wildtype ovaries when both cluster38C1 promoters are wildtype or deleted.