Fig. 1. Formation of a gas cavity around an impacting 20-mm-diameter steel sphere.
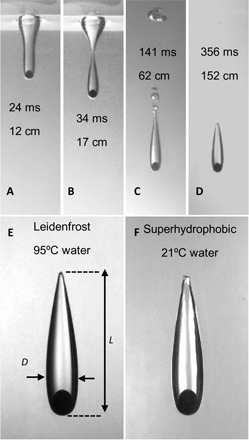
Snapshots from movie S2 showing (A and B) the formation of a gas cavity around a hot 20-mm Leidenfrost steel sphere at sphere temperature TS = 400°C as it enters a 2-m-tall tank containing water at 95°C and (C and D) the development and trajectory of the sphere-in-cavity structure at the indicated depths and times after entry. (E) A close-up of the steady-state gas cavity of length L and maximum diameter D formed around the 20-mm Leidenfrost steel sphere at TS = 400°C in 95°C water. (F) The steady-state gas cavity formed around a cold 20-mm superhydrophobic steel sphere at TS = 21°C in 21°C water.
