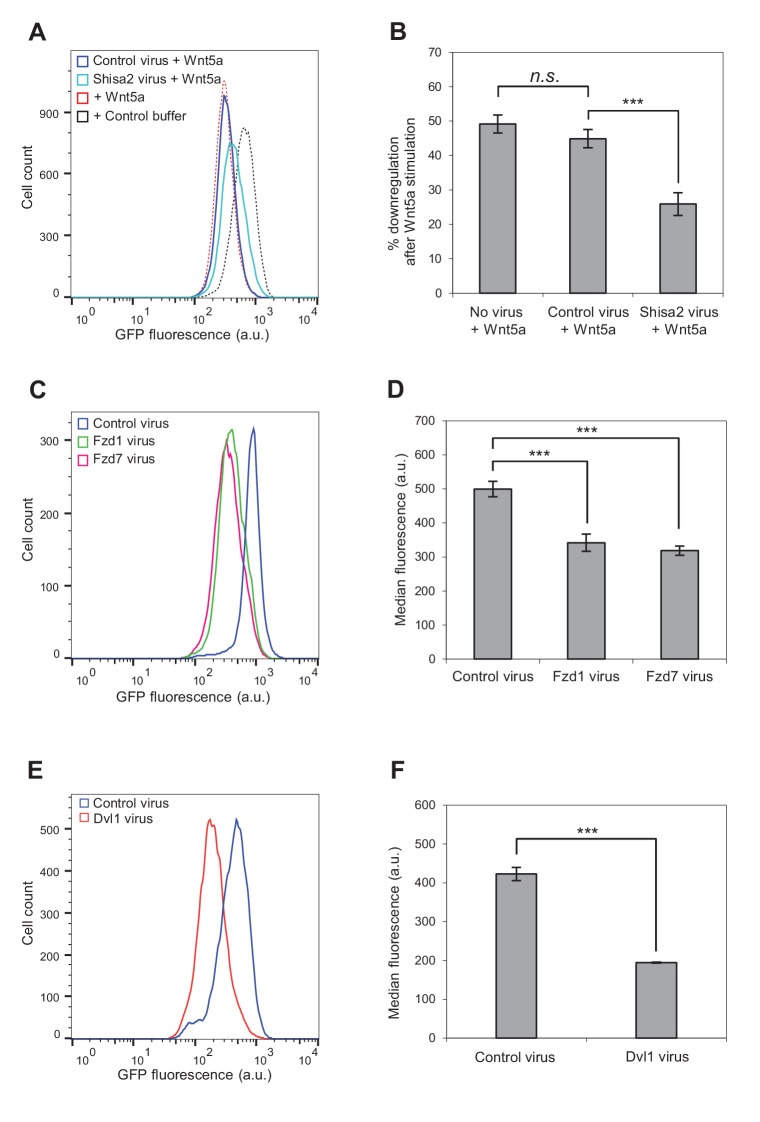
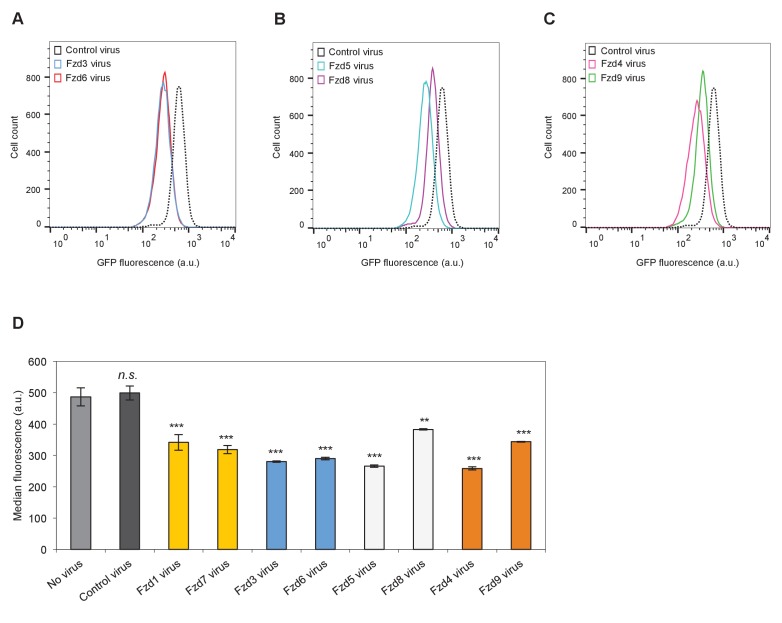
Figure 4. Involvement of Fzd and Dvl proteins in Kif26b degradation.
(A) Flow cytometry histograms depicting the effect of ectopic Shisa2 expression on the ability of Wnt5a to induce GFP-Kif26b degradation in the WRK reporter assay. Mouse Shisa2 was expressed via lentiviral transduction. A lentivirus expressing Cas9 was used as the control. The effect of Wnt5a or control buffer treatment on the WRK reporter line without virus infection is shown as a reference. (B) Quantification of effects of the control virus (Cas9) and the Shisa2 virus on the ability of Wnt5a to downregulate the GFP-Kif26b fluorescence in the WRK reporter assay, as shown in (A). Error bars represent ± SEM calculated from three technical replicates. t-tests were determined for the following comparisons: control virus vs. Shisa2 virus, p<0.001; control virus vs. no virus, p=0.0957 (not significant). (C) Flow cytometry histograms depicting the effect of ectopic Fzd1 or Fzd7 expression on GFP-Kif26b levels in the WRK reporter assay. Mouse Fzd1 and Fzd7 were expressed via lentiviral transduction. A lentivirus expressing Cas9 was used as the control. (D) Quantification of the median GFP-Kif26b fluorescence in the WRK reporter cell line infected with a Fzd1 virus, a Fzd7 virus, or a Cas9 control virus. Error bars represent ± SEM calculated from six technical replicates. t-tests were determined for the following comparisons: control virus vs. Fzd1 virus, p<0.001; control virus vs. Fzd7 virus, p<0.001. (E) Flow cytometry histograms depicting the effect of ectopic Dvl1 expression on GFP-Kif26b levels in the WRK reporter assay. Dvl1 was expressed via lentiviral transduction. A lentivirus expressing Cas9 was used as the control. (F) Quantification of the median GFP-Kif26b fluorescence in the WRK reporter cell line infected with a Dvl1-expressing virus, or a Cas9-expressing control virus. Error bars represent ± SEM calculated from three technical replicates. t-test was determined for control virus vs. Dvl1 virus, p<0.001.