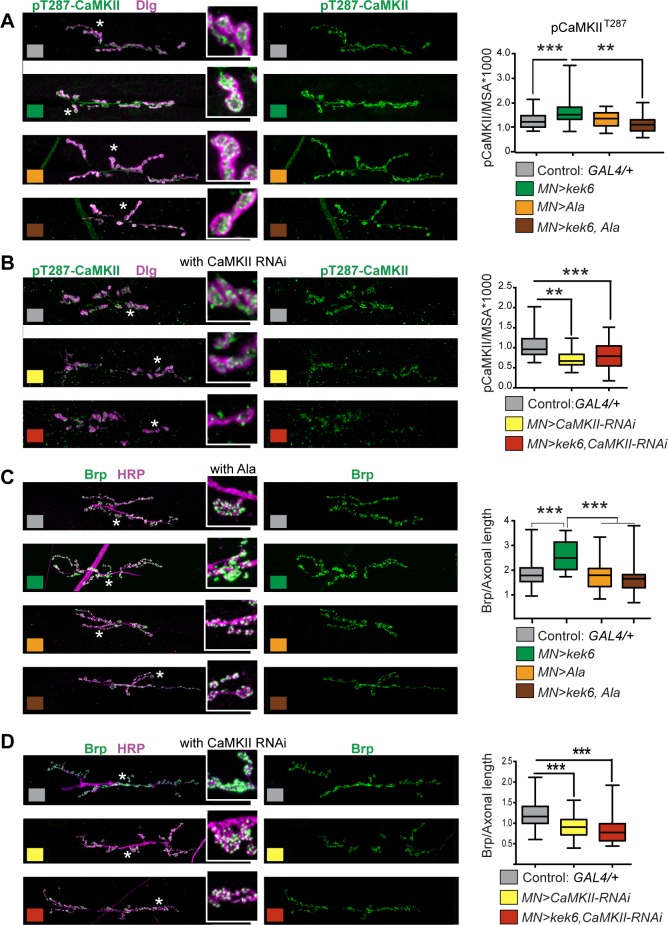
Fig 9. Kek6 activates CaMKII at the NMJ.
NMJs from A3-4 muscle 6/7 (left), and box-plot graphs (right), NMJs, labeled with anti-pCaMKIIT287 for the constitutively active form; anti-Dlg for post-synaptic boutons; anti-HRP for pre-synaptic axonal terminal length; anti-Brp for active zones. Brp and pCaMKIIT287 were quantified automatically with DeadEasy Synapse. Higher magnification details are of areas indicated by asterisks. (A, B) Over-expression of kek-6 in motoneurons increased pCaMKIIT287 levels, which was rescued with the over-expression of the CaMKII inhibitor Ala (A) or CaMKII RNAi knock-down (B) pre-synaptically. Kruskal-Wallis p<0.0001 and **p<0.01, ***p<0.001post-hoc Dunn for both graphs. (C,D) CaMKII inhibition with Ala (C) or knock-down with CaMKII-RNAi (D) rescued the increase in active zones caused by kek-6 over-expression. (C) One-way ANOVA p<0.000 and ***p<0.001 post-hoc Bonferroni, (D) Kurskal-Wallis p<0.0001 and **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 post-hoc Dunn’s. See S1 Table. N = 25–43 hemisegments. MN = motoneurons. Genotypes: (A-D) Control: w; D42GAL4/+. (A, C) w; D42GAL4/UASkek6RFP. w; D42GAL4/UASAla; w; D42GAL4/UASkek6RFP UASAla. (B, D) D42GAL4/UASCaMKIIRNAi. w; D42GAL4/UASkek6RFP UASCaMKIIRNAi.