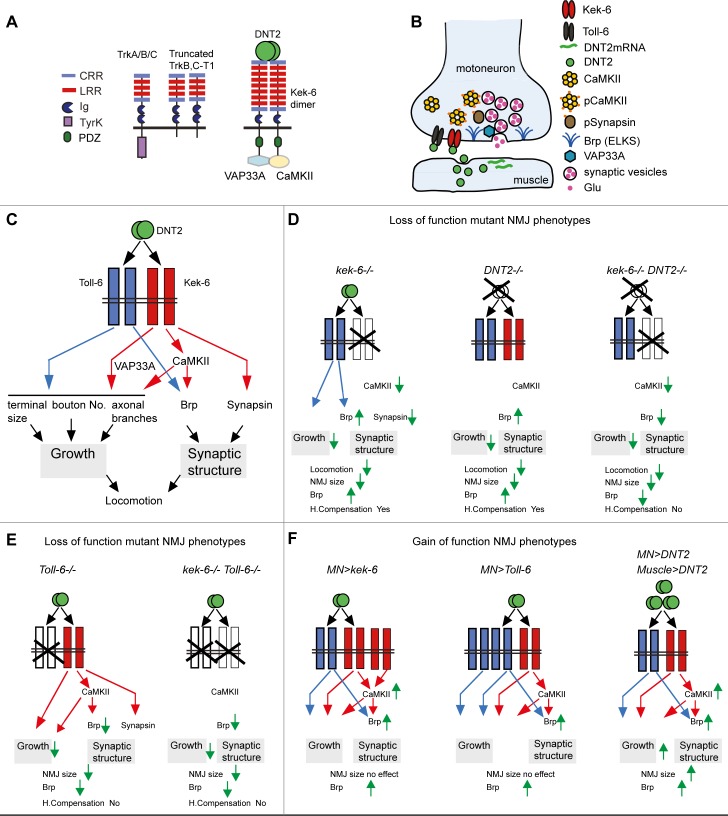
Fig 12. Retrograde DNT2 binds pre-synaptic Kek-6 activating CaMKII and regulating structural synaptic plasticity.
(A) Illustration of Kek-6 compared to Trk isoforms. DNT2 binds Kek-6, which functions via CaMKII and VAP33A downstream. (B) Pre-synaptic motoneuron terminal at the NMJ: DNT2 is produced at the muscle and secreted, binds pre-synaptic Kek-6, functioning via CaMKII and VAP33A downstream. DNT2 also binds Toll-6 which can interact with Toll-6. (C) The concerted functions of DNT2 and its two receptors Kek-6 and Toll-6 regulates NMJ growth and synaptic structure. Kek-6 functions via CaMKII and VAP33A downstream, the mechanism downstream of Toll-6 at the NMJ has not been investigated in this work. Red arrows: positive regulation by Kek-6; blue arrows: positive regulation by Toll-6. (D-F) Summary of the experimental evidence provided, green arrows indicate up- or down-regulation as a result or loss or gain function genotypes. Altering the levels of DNT2, Kek-6 and Toll-6 affects locomotion, NMJ growth and synaptic structure. Importantly, loss of both kek-6 and Toll-6 prevents homeostatic compensation of active zones, and whereas gain of function for kek-6 or Toll-6 is not sufficient to increase NMJ size, over-expression of DNT2 can. The data suggest that Kek-6 and Toll-6 function in concert as a receptor complex for DNT2, to regulate structural synaptic plasticity.