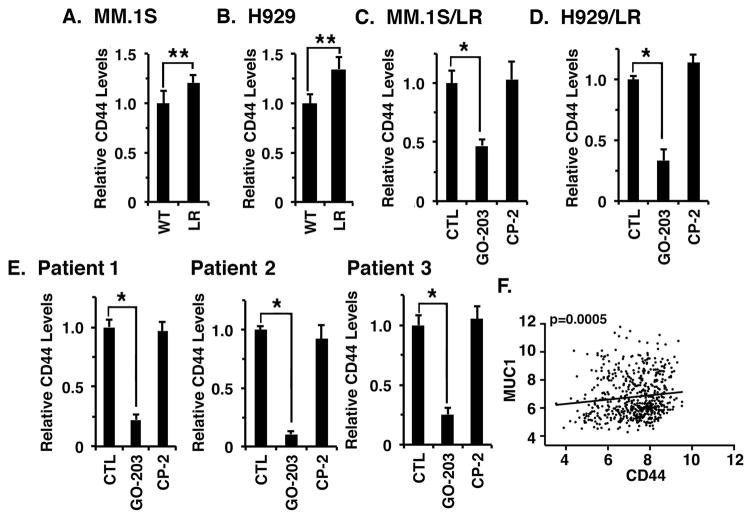
Figure 6. Targeting MUC1-C downregulates CD44 expression.
A and B. The indicated wild-type (WT) and lenalidomide (LEN) resistant (LR) MM.1S (A) and H929 (B) cells were analysed for CD44 expression by flow cytometry. The results are expressed as relative CD44 levels (mean±SD of 3 determinations) as compared to that obtained for WT cells (assigned a value of 1). C and D. MM.1S/LR (C) and H929/LR (D) cells were left untreated (CTL) and treated with 4 μM GO-203 or CP-2 for 72 h. The results are expressed as relative CD44 levels (mean±SD of 3 determinations) as compared to that obtained for CTL cells (assigned a value of 1). The results are representative of 3 independent experiments. E. Primary CD138+ MM cells from Patient 1 (LEN-sensitive), Patient 2 (LEN-resistant) and Patient 3 (LEN-resistant) were left untreated (CTL) and treated with 5 μM GO-203 or CP-2 for 72 h. The results are expressed as relative CD44 levels (mean±SD of 3 determinations) as compared to that obtained for CTL cells (assigned a value of 1). F. Microarray gene expression data from GEO dataset GSE2658 (n=559) was RMA normalized and the correlation between MUC1 and CD44 expression in MM patients was assessed by Spearman correlation, where p<0.05 was considered as statistically significant. * p<0.01; ** p<0.05.