Figure 4. Chloramphenicol Increases Trp-tRNATrp Level.
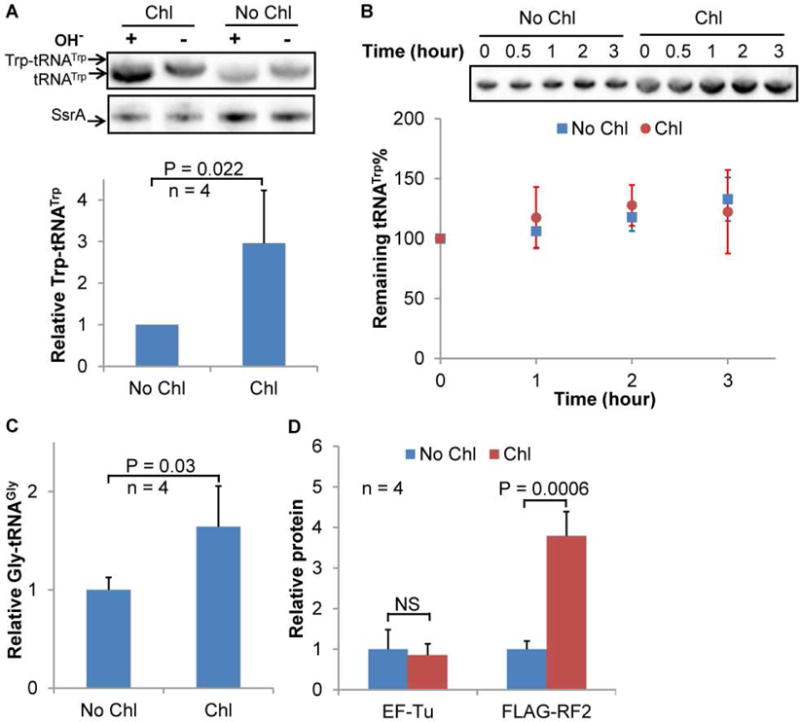
(A) Chl treatment increases the level of Trp-tRNATrp shown by acidic northern blotting. Total RNA was isolated from MG1655 cells grown in LB with or without 2 μg/ml Chl under acidic conditions, and treated with or without alkaline (OH−) before acid gel electrophoresis and northern blotting. Alkaline treatment causes deacylation of aminoacyl-tRNAs. Almost 100% of tRNATrp was aminoacylated without alkaline treatment. SsrA was used as an internal standard to calculate the relative concentration of Trp-tRNATrp. (B) Stability of tRNATrp with and without Chl. MG1655 cells grown in LB in the presence absence of Chl were treated with a high concentration of rifampicin to stop transcription. RNA samples were prepared at indicated time points following addition of Rif and subjected to northern blotting analysis. Chl increases the overall level of tRNATrp, but not the stability. (C) The level of Gly-tRNAGly was determined using acidic gel northern blotting as in Figure 4. (D) The protein levels of EF-Tu and FLAG-RF2 with and without Chl revealed by Western blotting. A FLAG tag is fused to the C-terminus of RF2 at the native chromosomal site. Data are represented as mean ± standard deviation.
