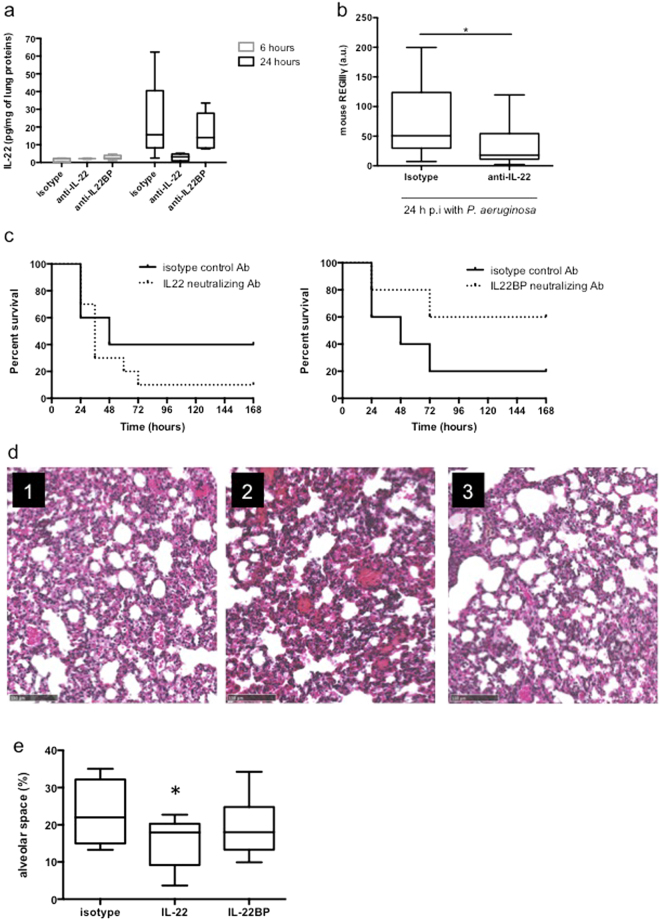
Figure 3.
IL-22 neutralisation enhances mice susceptibility and lung damage to PA. (a) IL-22 level assessment by ELISA in lung homogenates of IL-22 neutralised mice. Boxes represent median (interquartile range). Data are representative of two independent experiments (n = 6 per infected group). *p < 0.05 and n.s.: not significant compared with the sham group. (b) Impact of IL-22 neutralisation on REGIIIγ mRNA expression in total lungs of 6-hour infected mice. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments (n = 5). (c) Survival curves of infected mice treated with an isotype control antibody (solid line) or with an IL-22- neutralising antibody (left panel – dashed line) or with and IL22-BP neutralising antibody (right panel – dashed line). Survival rates are expressed as percentage and are representative of 2 independent experiments (anti-IL-22: n = 8 per group; anti-IL-22BP: n = 5 per group). (d) Lung histological analysis from infected mice treated with an isotype control antibody (panel 1), an IL-22- neutralising antibody (panel 2) or with an IL-22BP neutralising antibody (panel 3). Magnification × 100. Bar = 100 μm. Data are representative of two independent experiments (n = 3). (E) Alveolar space quantification by SIOX analysis of histology slides presented in (d) (3 mice per slide. 4 fields per slide). *p < 0.05 compared with the isotype group.