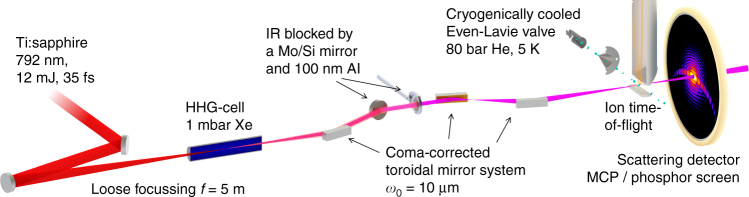
Fig. 1.
Scheme of the experimental setup. A Ti:sapphire laser with 792 nm central wavelength and 35 fs pulse duration is used for the generation of high harmonics. Up to 12 mJ are loosely focused into a xenon-filled cell, where the extreme ultraviolet (XUV) pulses are produced. The copropagating near-infrared (NIR) beam is removed via a Mo/Si mirror and a thin aluminum filter. The beam is focused to a small spot (ω0 = 10 μm) using a coma-correcting system of three gold-coated toroidal mirrors26. A pulsed jet of helium nanodroplets ( ≈ 400 nm) is overlapped with the XUV focus. The overlap is optimized by monitoring the formation of He+ ions using an ion time-of-flight spectrometer. The scattering signal is amplified by a pulsed MCP and converted to optical photons on a phosphor screen. The single-shot diffraction images are captured with an out-of-vacuum camera (not depicted)