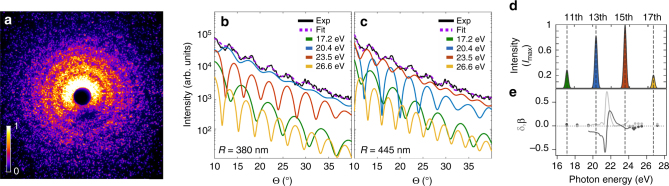
Fig. 2.
Multicolor analysis of the diffraction images. a Measured bright scattering image (center part of the detector, intensity in arbitrary units) from a spherical droplet with a pronounced concentric ring pattern. b, c Multicolor Mie fits (dashed purple) of the extracted radial intensity profile (solid black) from a as obtained via a simplex optimization (see “Methods” section) of the individual harmonic contributions to the profiles (color-coded in green, blue, red, and yellow). The results illustrate that two qualitatively different solutions yield comparably small residuals. The two solutions indicate that either the 13th harmonic b or the 15th harmonic c dominates. The resulting refractive indices of these and all other fits are given in Supplementary Fig. 4. d Measured average extreme ultraviolet spectrum of the high harmonic radiation. e Sketch of the energy-dependent refractive indices of bulk liquid helium in the vicinity of the helium 1s–2p transition, assembled from bulk liquid helium measurements31, 32 (solid lines, color-coded in light-gray and dark-gray) and tabulated values (scatter, NIST database, http://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/FFast/html/form.html)