Figure 3.
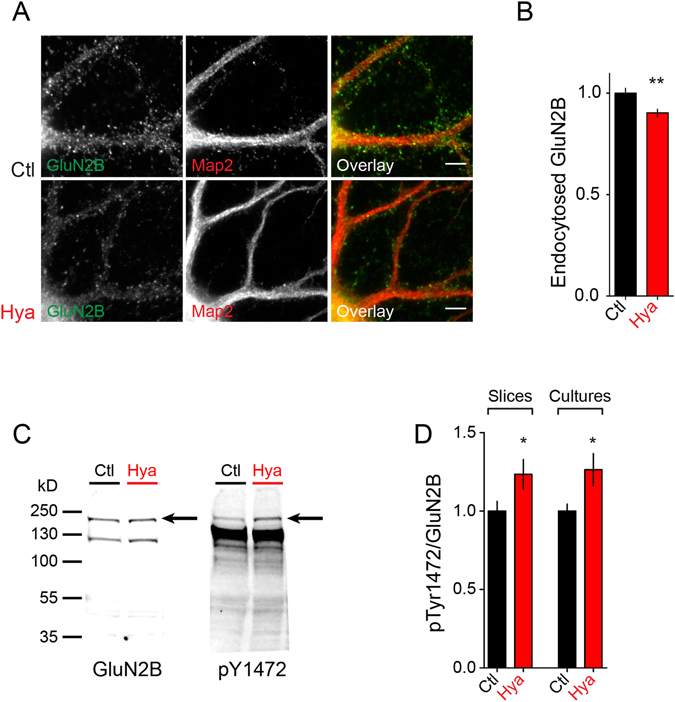
ECM digestion increases p1472-GluN2B level and decreases the endocytosis of GluN2B. (A)Dissociated hippocampal cultures at DIV21-24 were treated with Hya over night and endocytosed GluN2B (green) was quantified using Map2 staining as mask (red). (B) There is less endocytosis of GluN2B after ECM removal within 30 minutes (Ctl 1.00 ± 0.02, n = 79; Hya 0.9 ± 0.02, n = 80; average ± SEM, Unpaired t-test, **P = 0.0015. Scale bar: 5 µm). (C) Quantitative WB from lysates of acute hippocampal slices treated with Ctl or Hya probed with an antibody against pGluN2B pTyr1472 (AP2 binding site) and GluN2B. (D) Quantification of WB of acute hippocampal slices and cortical cultures (DIV 21–24) revealed that the amount of phosphorylated GluN2B, normalized to the total amount of GluN2B, is increased after Hya treatment (overnight for cultures, 3 h for slices; slices: Ctl 1.00 ± 0.06, n = 4; Hya 1.23 ± 0.09, n = 4; cultures: Ctl 1.00 ± 0.05, n = 9; Hya 1.26 ± 0.1, n = 9; Unpaired t-test, cultures: P = 0.0332, slices P = 0.0837, ***P < 0.0001).
