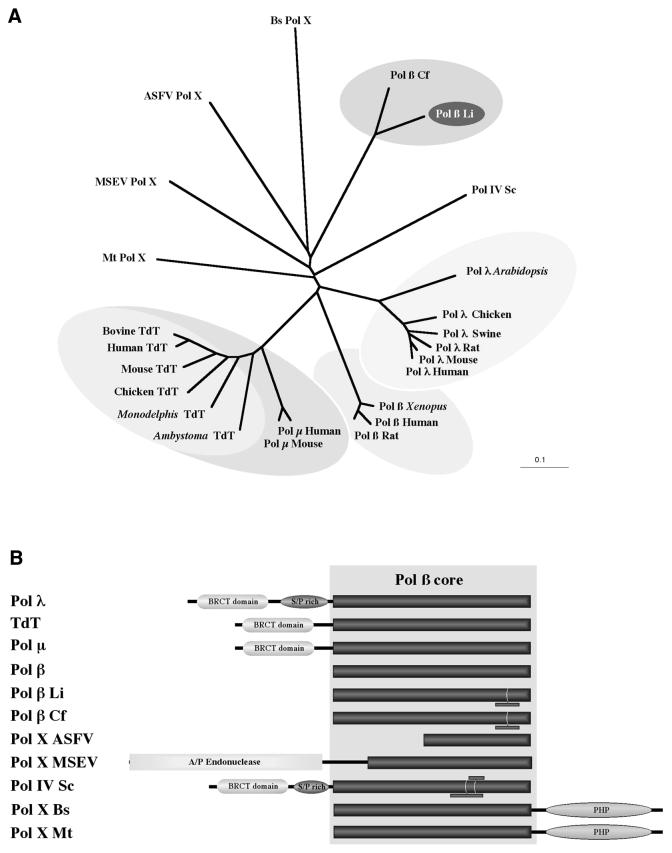
Figure 8.
The Pol X family of DNA polymerases. (A) Phylogenetic tree representing the evolutionary distances among the different members of the Pol X superfamily. The data was obtained by CLUSTALW alignment of a polypeptide segment corresponding to the most conserved segment of the Pol β core, forming the polymerization active site (see Materials and Methods). The DNA polymerases included are: Pol λ from different species of plant and animals; Pol µ from human and mouse; TdT from different vertebrates; Pol β from human, rat, X.laevis and C.fasciculata (Cf); Pol X from ASFV; Pol X from MSEV; Pol IV from S.cerevisiae (Sc); Pol X from B.subtilis (Bs); Pol X from M.thermoautotrophicum (Mt). (B) Domain organization of the different members of the Pol X family. Enzyme nomenclature is as shown in (A). The generally conserved Pol β core is shown as a dark box. The presence of additional sequences is indicated by small bars. The APE predicted at the N-terminus of the MSEV Pol X is boxed in gray. Additional domains, as the BRCT, Ser-Pro rich domain and PHP domain are also indicated.