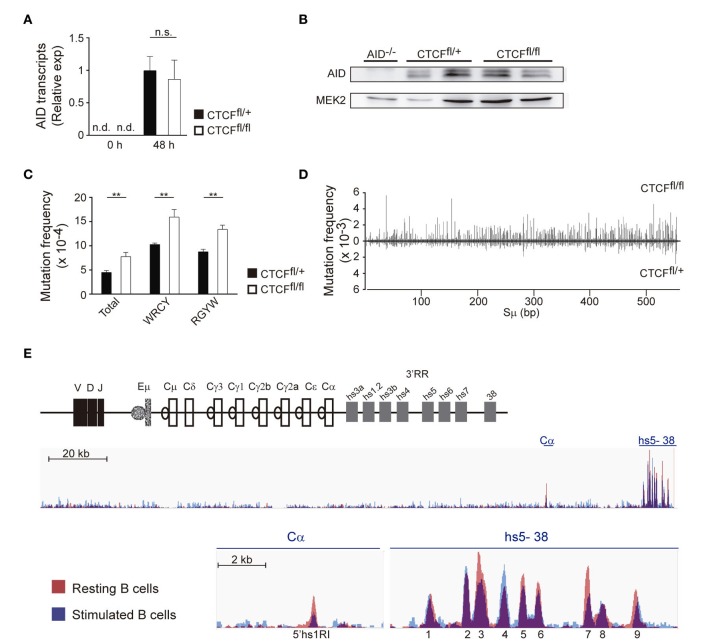
Figure 4.
CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) deletion increases S region somatic mutation and germline transcription. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) expression in spleen B cells from CTCFfl/+ (n = 7) and CTCFfl/fl (n = 6) mice 48 h after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) + IL-4 stimulation. (B) Western blot analysis of AID in B cells from AID−/−, CTCFfl/+, and CTCFfl/fl mice after 48 h of LPS/IL-4 stimulation. Mek2 is shown as a loading control. (C) Analysis of AID mutagenic activity by next-generation sequencing (32). DNA was isolated from splenic B cells 48 h after LPS + IL-4 stimulation, amplified by PCR with specific primers and analyzed by next-generation sequencing. Graphs show total mutation frequency, mutation frequency at C or G in WRCY/RGYW hotspot motif in CTCFfl/+ (n = 3) and CTCFfl/fl (n = 3) mice. p(total) = 0.0039; p(WRCY) = 0.0037; p(RGYW) = 0.0015. (D) Distribution of mutations along the sequenced Sμ region in CTCFfl/+ (n = 3) and CTCFfl/fl (n = 3) mice. Mutation frequency at each position is shown. (E) CTCF-binding at the IgH locus in resting and stimulated B cells (data from GSE43594).