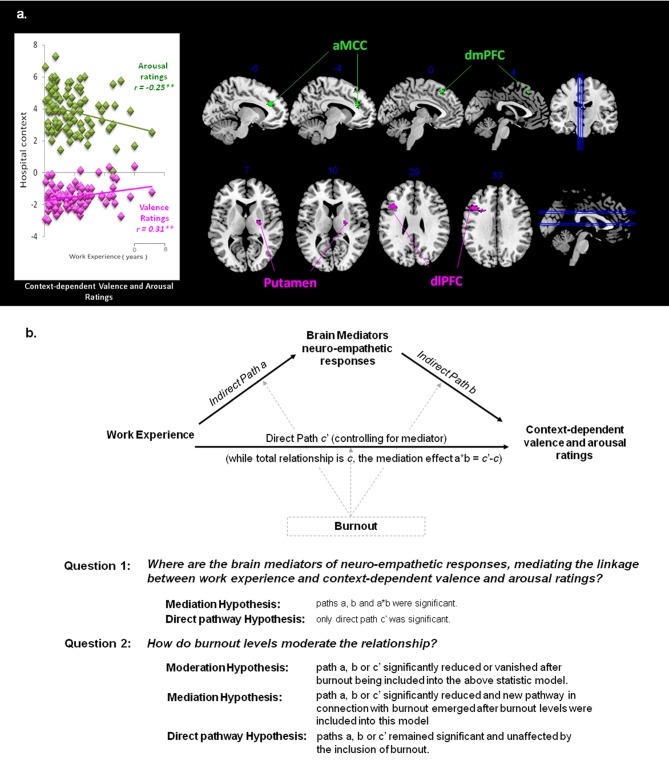
Figure 3.
Hypothesis for mediation analysis. (A) Context-dependent valence and arousal ratings. The correlation between subjective ratings and work experience was specific to the context. Significant correlations occurred between context-dependent subjective ratings and neuro-empathetic reaction (Pain vs. Neutral). Suprathreshold voxels (p < 0.05 corrected for voxel-wise comparisons) are displayed across four coronal and sagittal sections on the ch2bet template, using MRIcron software (http://www.sph.sc.edu/comd/rorden/mricron/). The hemodynamic response in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC; −14, 32, 28) and dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (dmPFC; −6, 26, 52) was significantly negatively correlated with arousal ratings (shown in green), whereas the response in the putamen (24, −8, 10) and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC; −42, 18, 30) was positively correlated with valence ratings (shown in magenta). These areas are the main ROIsfor the mediation analysis. (B) Mediation Model and Hypotheses. While observing the context-dependent valence and arousal ratings, we selected work experience as the predictor variable, and performed analyses to test if the above ROIs were the mediators of the linkage between work experience and subjective ratings of valence and arousal. Whether and how each scale of Burnout moderates the existing model and area of interest are considered as well.