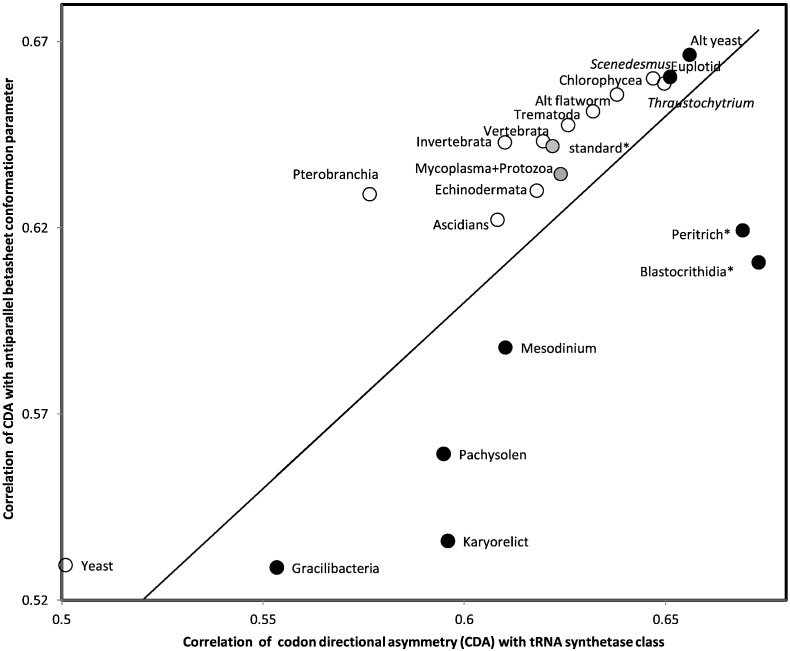
Fig. 3.
Correlation between antiparallel betasheet conformation parameter of amino acids and mean directional asymmetry (CDA) of codons assigned to that amino acid as a function of the correlation between CDA and the tRNA synthetase class for the corresponding amino acid for different genetic codes. Correlations are Pearson correlation coefficients. Filled/open circles are nuclear/mitochondrial genetic codes, shaded circles are for genetic codes existing in nuclei and mitochondria. The line indicates y = x. Nuclear genetic codes tend to optimise the association between CDA and tRNA synthetase classes, mitochondrial genetic codes tend to optimise the association between CDA and the antiparallel betasheet conformation parameter. Most mitogenome-encoded proteins are transmembrane proteins, hence antiparallel betasheets are particularly frequent in these proteins. Hence genetic code evolution optimises the CDA-antiparallel betasheet association in mitochondria. Open circles: mitochondrial genetic codes; filled circles: nuclear genetic codes; shaded circles: genetic codes used in nuclei and mitochondria.