Figure 2.
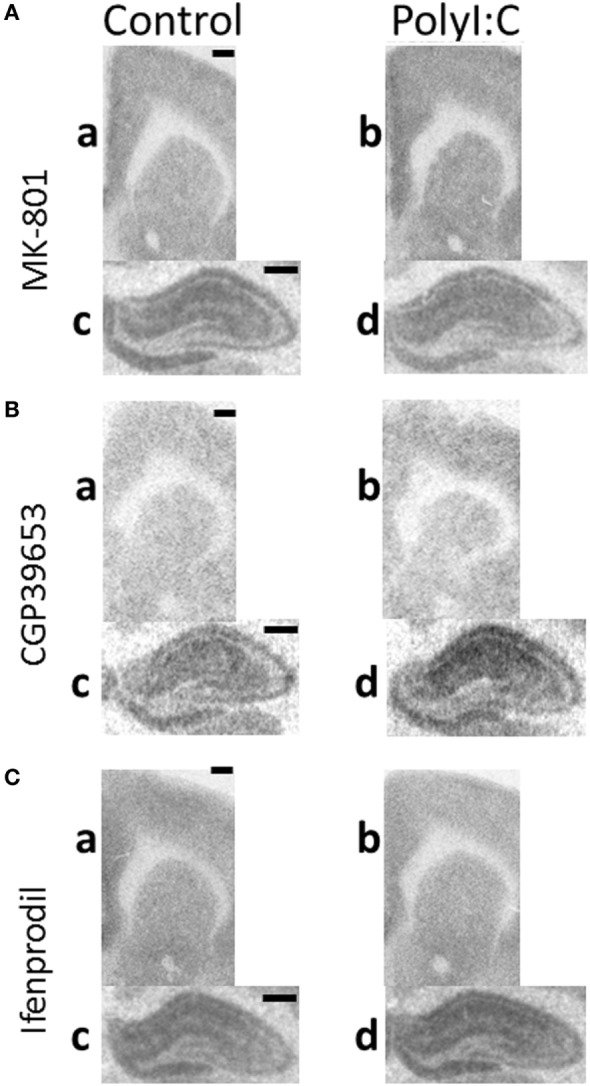
Representative autoradiographs of regions from maternal immune activation offspring. Coronal sections from adult (postnatal day 63–91) male offspring from vehicle (control: a,c) or polyI:C (b,d) treated dams were processed with tritiated radioligands to detect (A) N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) channel (MK-801), (B) NR2A (CGP39653), and (C) NR2B (Ifenprodil) binding in (a,b: ~2.50 mm bregma) cortical, striatal, and (c,d: ~−3.10 mm bregma) hippocampal regions. (A) PolyI:C offspring showed significantly increased NMDAR channel binding in (a,b) cingulate and striatum, but not (c,d) hippocampal regions. (B) PolyI:C offspring showed significant increases in NR2A binding overall in all quantified regions. (C) PolyI:C offspring showed no significant change in NR2B binding overall in any quantified region. Scale bars represent 500 µm.
