Fig. 4.
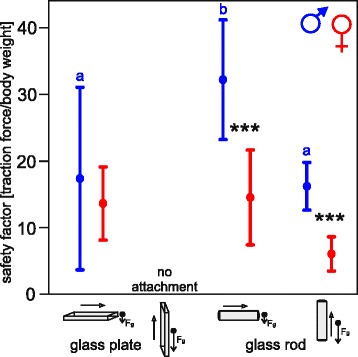
Safety factors generated by male and female Monochamus alternatus on a glass plate and glass rod; scatterplot showing column means and standard deviations. Attachment failed on vertically oriented, flat glass. Arrows with unfilled heads point to the direction of traction, and arrows with filled heads point to the direction of acting gravity. Dots show means with standard deviations (lines). The asterisks mark statistical differences between males (blue) and females (red) on horizontal flat glass: Mann-Whitney test, T = 26, p = 0.841, on horizontal glass rod: t-Test, t = −3.5, p = 0.009, and on vertical glass rod: t-Test, t = −4.6, P = 0.002; different letters indicate statistical differences between substrates in males (one-way ANOVA, F2,13 = 4.2, P = 0.04, Fisher LSD method). Values not differ significantly between substrates in females (one-way ANOVA, F2,13 = 3.7, P = 0.056)
