Fig. 8.
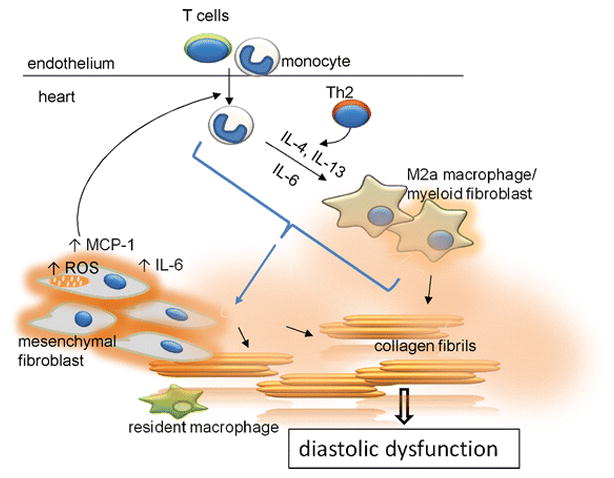
The two way interaction between infiltrating leukocytes and mesenchymal fibroblasts in the aging mouse heart. The dysregulated mesenchymal fibroblasts produce higher levels of ROS that promote expression of MCP-1 and IL-6. Secreted MCP-1 attracts leukocyte infiltration into the heart. Infiltrating monocytes polarize into alternatively activated M2a macrophages/myeloid fibroblasts in response to Th2 products (IL-4 and IL-13) and IL-6 (derived at least partially from dysregulated mesenchymal fibroblasts). Both types of fibroblasts (mesenchymal and myeloid) secrete collagen. Excessive collagen production by mesenchymal fibroblasts is controlled by the infiltrating leukocytes; without input from leukocytes/monocyte-derived macrophages, mesenchymal fibroblasts remain unactivated and do not overproduce collagen. Augmented collagen production contributes to fibrosis and diastolic dysfunction. Resident macrophages do not play an apparent role in this process.
