Figure 1. Mechanically activated currents recorded in nociceptive-like and non-nociceptive-like DRG neurons acutely dissociated from rats.
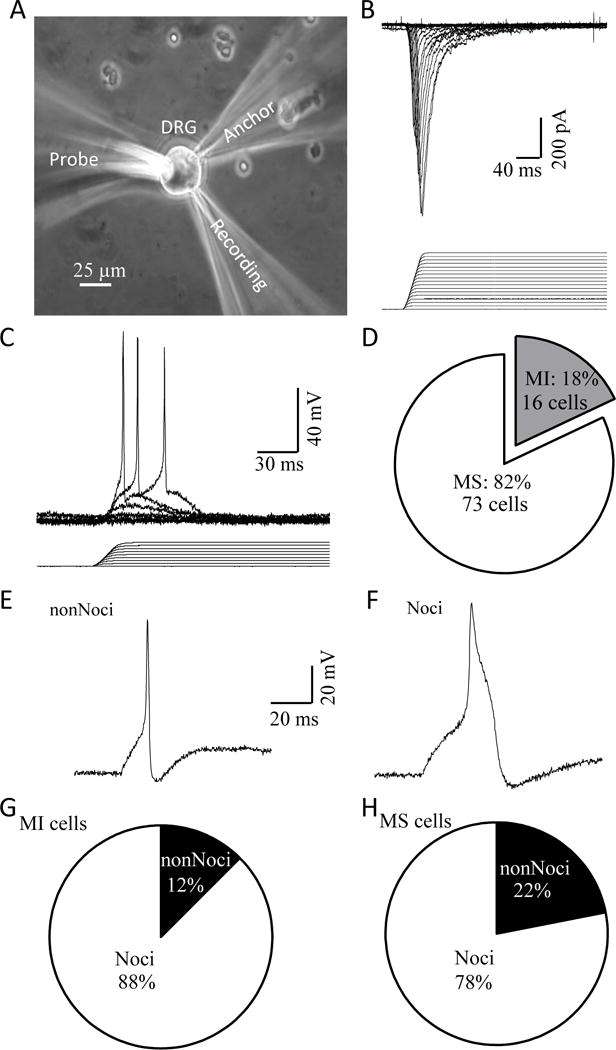
A) Experimental setup for patch-clamp recordings of MA currents from acutely dissociated rat DRG neurons. B) A set of sample traces of MA currents in a DRG neuron (upper) evoked by stepwise membrane displacements with increment of 1 μm (lower). C) Example of mechanically evoked membrane depolarization and action potential firing in a DRG neuron. D) Graph shows the fractions of DRG neurons that are mechanically sensitive (MS) showing MA currents (white, 73/89) and mechanically insensitive (MI, 16/89). E) An example of the action potential shape of a non-nociceptive-like (nonNoci) MS DRG neuron. F) An example of the action potential shape of a nociceptive-like (Noci) MS DRG neuron. G) Fractions of MI neurons that are nonNoci (2/16) and Noci neurons (14/16). H) Fractions of MS neurons that are nonNoci 16/73) and Noci (57/73) neurons.
