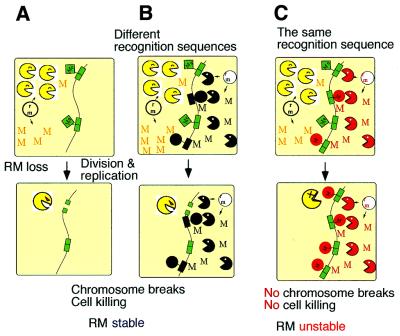
Figure 6.
Competition for recognition sequences between RM gene complexes. (A) The cell contains one plasmid with an RM gene complex. When the plasmid (and thus also the RM gene complex) is eliminated from the cell, the modification enzyme is diluted and this leads to cell death by post-segregational killing. (B) The cell contains two plasmids, each with an RM gene complex that has a different sequence specificity. When either of the plasmids is lost together with its RM gene complex, the cells die due to post-segregational cell killing. Both of the RM gene complexes can enjoy stabilization. The situation is stable. (C) The cell contains two plasmids, each with an RM gene complex that has the same sequence specificity. Loss of either of the plasmids together with its RM gene complex does not lead to cell killing because the other RM system modify the recognition sites on the host chromosome. The two RM gene complexes cannot simultaneously enjoy stabilization. The situation is unstable.