FIGURE 6.
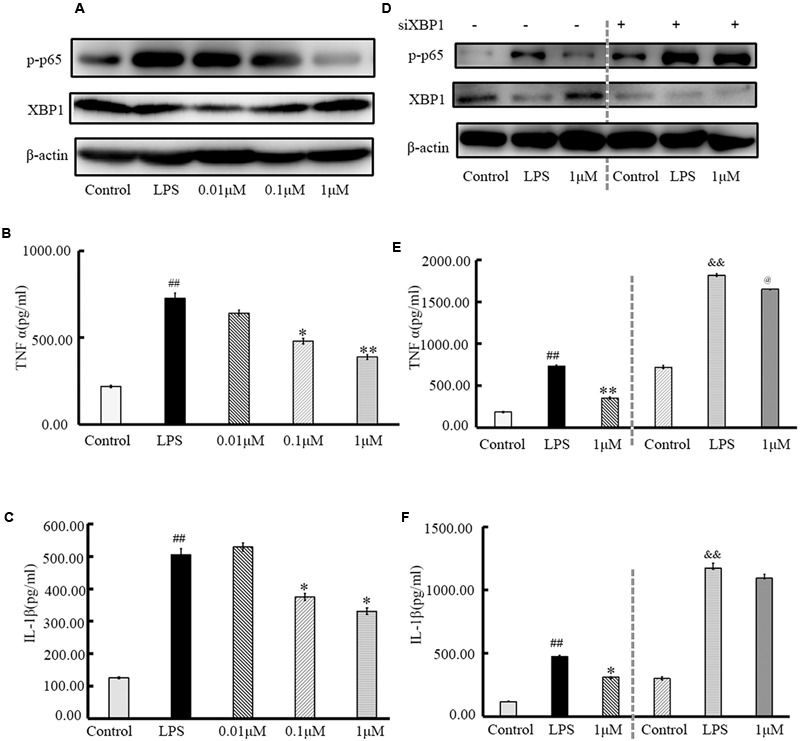
Treatment with (±)-8-ADC inhibits XBP1, NF-κB, and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in IEC6 cells. (A) Western-blot of IEC6 cells. The effect of (±)-8-ADC on NF-κB p-p65 phosphorylation was determined by Western-blot. (±)-8-ADC inhibited NF-κB p65 phosphorylation in IEC6 cells. (B,C) Effect of (±)-8-ADC on (B) TNF-α and (C) IL-1β production. Following stimulation with 5 μg/ml LPS for 24 h, (±)-8-ADC decreased TNF-α and IL-1β expression in IEC6 cells in a dose-dependent manner. (D) Western-blot of siXBP1 in IEC6 cells. In the negative control group, siXBP1(–), (±)-8-ADC inhibited p-p65 expression and increased XBP1 expression in IEC6 cells in a dose-dependent manner. Conversely, inhibition effect of (±)-8-ADC was reduced by silencing XBP1 in IEC6 cells. Compared with the negative control group, siXBP1(–), p-p65 was notably increased in siXBP1(+) groups. (E,F) The effect of (±)-8-ADC on (E) TNF-α and (F) IL-1β production following silencing of XBP1 in IEC6 cells. Compared with the negative control group, siXBP1(–), secretion of TNF-α and IL-1β were significantly higher in the siXBP1(+) groups. Each experiment was repeated three times. ##p < 0.01 compared with the control group; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 compared with the LPS group. &&p < 0.01 compared with the “control+si” group, @p < 0.05 compared with the “LPS+si” group.
