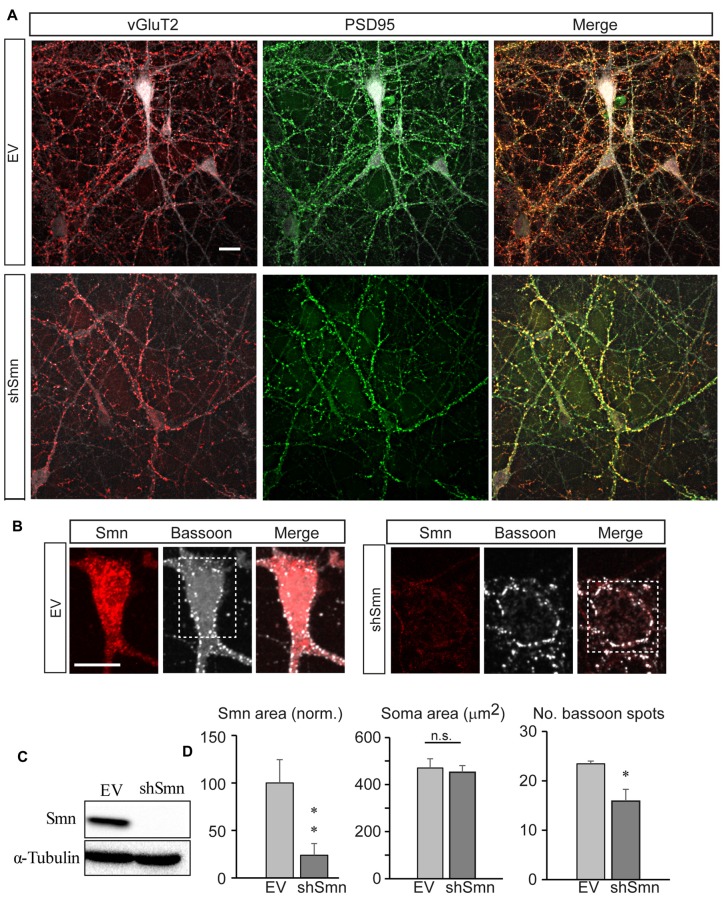
Figure 1.
Smn-deficient spinal motoneurons in culture establish less synapse contacts than empty vector (EV)-transduced neurons. (A) Embryonic mouse motoneurons in primary culture develop an extended neural network with numerous synaptic contacts at DIV12, both in EV and shSmn-transduced cultures, as visualized by confocal microscopic Z-projections. Axosomatic and axodendritic synapses appear as punta (red, anti-vGLUT2; green, anti-PSD95. Merged images are also shown. (B) Examples of immunofluorescence for Smn (red) and bassoon (white) at the soma of EV and shSmn-transduced motoneurons. (C) Western blot for Smn content in EV and shSmn-transduced cultures. (D) Comparison of the Smn fluorescence surface area, somatic total surface area, and number of bassoon spots in EV and shSmn-transduced cultures. The Smn signal is significantly decreased in Smn-deficient motoneurons (p = 0.008. two-tail unpair t-test). The mean number of bassoon spots is also low in Smn-deficient motoneurons (16.1 ± 1.6 spots; 48 neurons, three independent experiments) in comparison with motoneurons in EV cultures (23.4 ± 2.1 spots; 31 neurons, 31 neurons, three independent experiments; *p = 0.006, two-tail unpair t-test). Error bars represent SEM. Calibration bars: 20 μm.