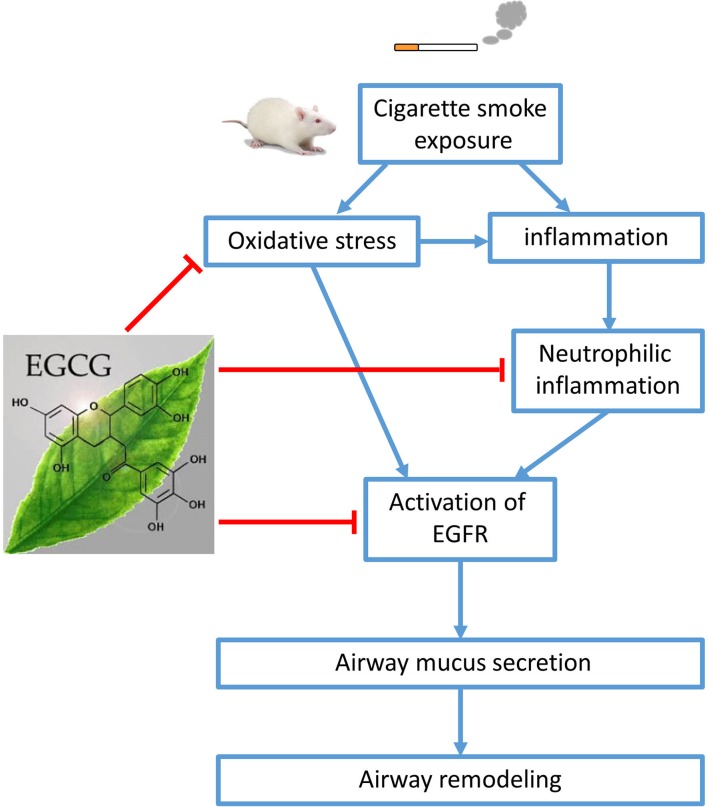
FIGURE 7.
Schematic diagram. Cigarette smoke (CS) exposure causes oxidative stress, inflammation, and airway mucus production. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) attenuated CS-induced oxidative stress, neutrophilic airway inflammation, and airway mucus production in rat lungs probably via the inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling pathway, leading to amelioration of airway remodeling.