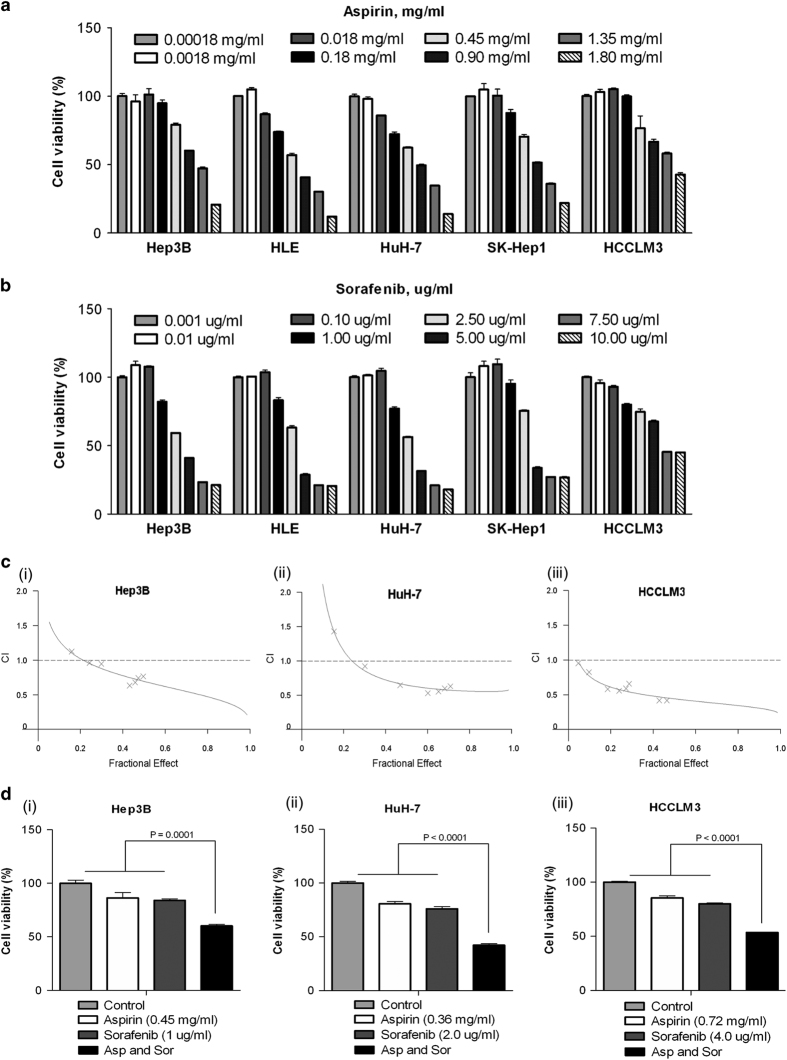
Figure 1.
The inhibitory effects of aspirin and sorafenib and synergistic inhibition effects of combined aspirin and sorafenib in different liver cancer cells in vitro. (a and b) Dose-escalation effects of aspirin (a) and sorafenib (b) on cell viability in five HCC cell lines was determined with MTS assays. (c) Synergistic curve of interactions between aspirin and sorafenib in Hep3B (i), HuH-7 (ii) and HCCLM3 (iii) cells. Cells were treated with aspirin or sorafenib either individually or in combination over a range of concentrations at a fixed ratio for 24 h. After the cell viability was determined with MTS assays under each condition, the combination index was calculated as described in the Materials and Methods. CI values of less than one are considered synergism. (d) Combined effects of aspirin and sorafenib in Hep3B (i), HuH-7 (ii) and HCCLM3 (iii) cells. Cells were exposed to study agents either individually or in combination at indicated concentrations for 24 h and cell viability was assessed using MTS assays. All data were plotted as the percentage of the control (DMEM) treated cells. Points, mean; bars, S.E. (n=3).