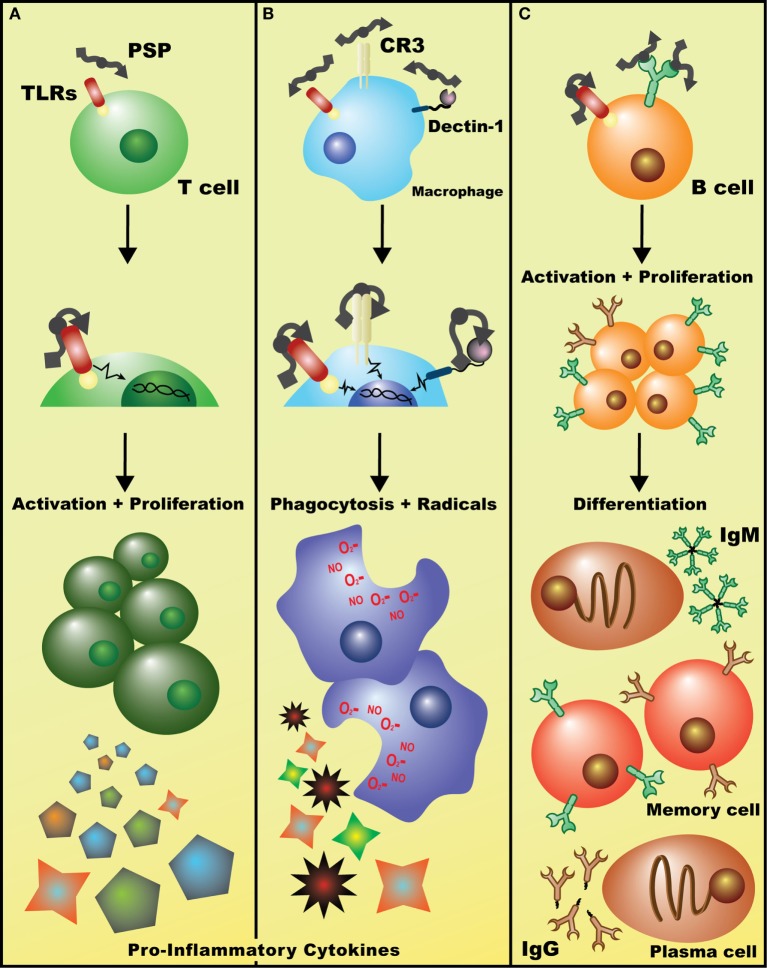
Figure 2.
Potential mechanisms of immuostimulatory effects of Coriolus versicolor. (A) Detection of polysaccharopeptide (PSP) by TLR(s) (and perhaps other receptors) on T lymphocytes initiates signaling cascades, such as the p38 MAPK pathway, leading to enhanced T cell proliferation and the release of largely pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-2 and IFN-γ. (B) Binding of PSP to any/all of Dectin-1, CR3, or TLRs on macrophages leads to the activation of genetic events that increase phagocytic activity and induces the production of oxidative radicals and cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α. (C) Recognition of PSP by the BCR leads to B cell activation, clonal proliferation, and eventual differentiation into IgM+ or IgG+ plasma and memory B cells. Alternatively, PSP may be acting on B cells in a similar fashion to T cells, non-specifically activating them through TLR(s) and leading to a general increase in polyclonal IgM and IgG levels (data not shown).