Table 1. Formal Analogy of the Description of FRET and Anisotropy for Homogeneous Quenching/Rotation in the Absence of Conformational Dynamicsa.
| observables | FRET | anisotropy |
|---|---|---|
| specific fluorescence intensity decays | fD|D(DA)(t) | 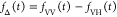 |
| fD|D(D0)(t) | 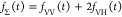 |
|
| intensity-independent quantifier | 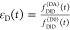 |
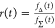 |
| species fraction of no FRET molecules/residual anisotropy | xnoFRET | r∞ |
| direct interpretation of intensity-independent quantifier | εD(t) = xnoFRET+∑ixRET(i)e–kRET(i)t | 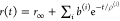 |
| steady-state quantifier by time-resolved measurements | 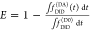 |
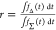 |
| derived steady-state values for single exponential decays | 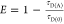 |
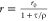 |
E is the FRET efficiency eq 1; kRET is the rate constant of the FRET process eq 9. τD(0) = 1/kD is the lifetime of the donor in the absence of an acceptor, and τD(A) = 1/(kD + kRET) is the lifetime of the donor in the presence of an acceptor. εD(t) is the FRET-induced donor decay. The letters V (vertical) and H (horizontal) represent the polarization of the excitation (first letter) and detection (second letter), respectively. Ideally, the time-resolved anisotropy decay r(t) is obtained by the difference fΔ and the sum f∑ of the experimental measurable intensity decays fVV and fVH. r is the steady-state anisotropy. ρ is the rotational correlation time.
