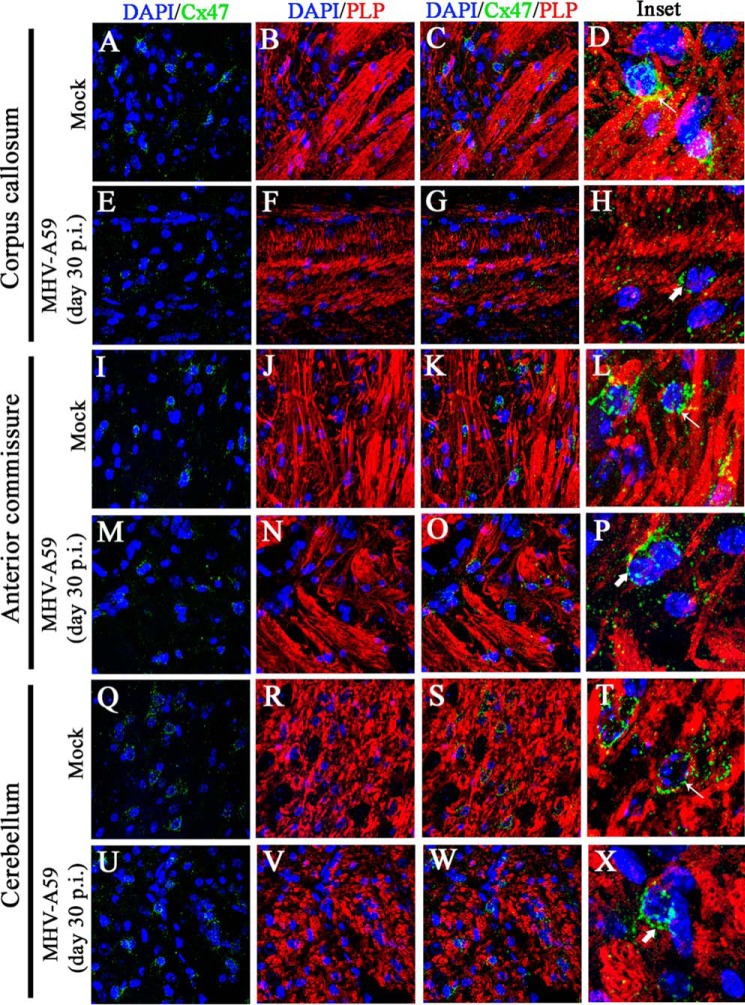
Figure 12.
Loss of Cx47 staining was associated with loss of PLP staining in chronic phase. Brain sections obtained from mock- and MHV-A59–infected mice were immunolabeled for Cx47 (green) and myelin marker, PLP (red). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). In mock-infected mice, Cx47 showed the characteristic stain at oligodendrocytic perikarya, specifically in and around the white-matter regions of brain (e.g. the corpus callosum (A and C), anterior commissure (I and K), and cerebellum (Q and S)). Prominent and profuse PLP staining was observed in normal corpus callosum (B and C), anterior commissure (J and K), and cerebellum (R and S). Insets show perikaryonic Cx47 staining observed in parallel to the PLP-stained myelinated axon fibers (D, L, and T (thin arrow)). MHV-A59–infected mice showed disrupted Cx47 staining, specifically in the corpus callosum (E and G). Anterior commissure (M and O) and cerebellum (U and W) showed Cx47 staining, which appeared to be normal, but the number of Cx47-positive puncta was marginally reduced. The PLP staining was reduced significantly in specific areas of the corpus callosum (F and G), but only marginal loss was evident in anterior commissure (N and O) and cerebellum (V and W). The insets show the altered expression pattern of Cx47 (H, P, and X (thick arrow)). Depletion of Cx47 staining was noticeably associated with the loss of PLP staining in the corpus callosum (H).