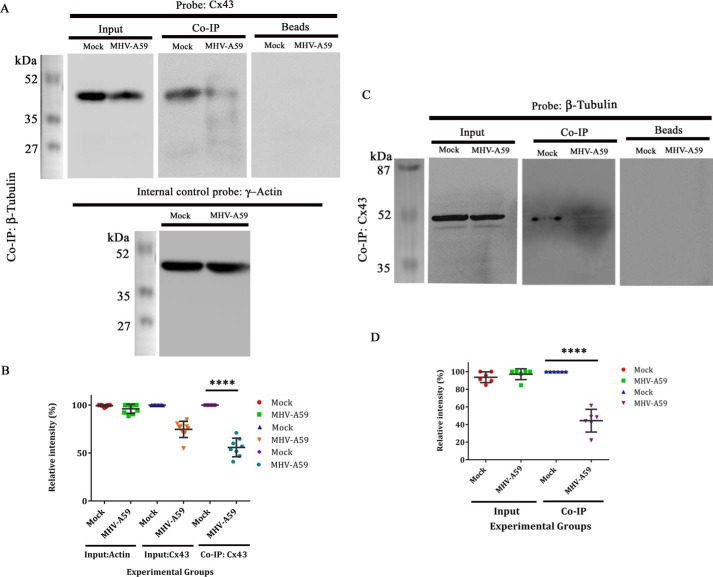
Figure 7.
Reduction in Cx43–β-tubulin interaction in protein level upon virus infection. Primary astrocytes were either mock-infected or infected with MHV-A59 at an MOI of 2. Proteins were extracted, followed by immunoprecipitation with monoclonal anti- β-tubulin antibody and subjected to immunoblot analysis using polyclonal anti-Cx43 antibody (detected at nearly 43 kDa). γ-Actin was used as a loading control (detected at nearly 42 kDa). Inputs showed reduction of total Cx43 upon MHV-A59 infection, where γ-actin expression was not altered. Upon co-IP, substantial reduction in tubulin-associated Cx43 was observed in the MHV-A59–infected cells, compared with the mock-infected cells. Beads, used in preclearing, showed no signal upon probing with anti-Cx43 (A). Densitometric analysis showed that Cx43, associated with β-tubulin, was reduced ∼44.25% in MHV-A59–infected cells, compared with the mock-infected cells (B; ****, p < 0.0001; t test). Similarly, the virus- and mock-infected cells were co-immunoprecipitated with polyclonal anti-Cx43 antibody and probed for β-tubulin using monoclonal anti- β-tubulin antibody (detected at nearly 50 kDa). β-Tubulin was expressed in equal amount in mock– and MHV-A59–infected cells. Cx43-associated β-tubulin signal was down-regulated significantly in virus-infected cells (C). Densitometric analysis showed that β-tubulin, associated with Cx43, was depleted ∼55.61% upon virus infection (D; ****, p < 0.0001; n = 3; t test). Error bars, S.D.