Figure 1.
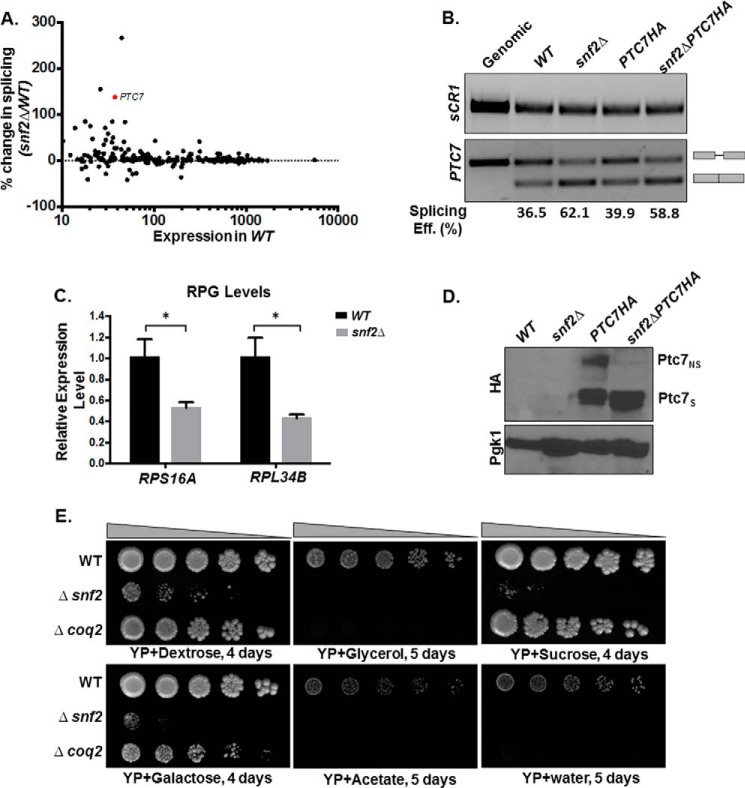
Deletion of SNF2 enhances splicing of PTC7 and the steady-state levels of the short Ptc7 protein isoform. A, deletion of SNF2 enhances splicing of a subset of yeast RNAs, including PTC7. The scatter plot shows changes in splicing of individual introns in snf2Δ yeast over WT plotted against expression in WT. Percentage change in splicing is calculated as 100 × (S.E. in snf2Δ − S.E. in WT)/(S.E. in WT). PTC7 is represented by the red dot. B, expression and splicing of PTC7 in WT and snf2Δ yeast with HA-tagged and untagged Ptc7. Semiquantitative analysis of splicing efficiency of PTC7 mRNA is indicated below each lane. sCR1 served as an internal control. Gray bars, exons of the RNA; thin gray line, intron. C, RT-qPCR measurement of selected intron-containing RPG transcripts between WT and snf2Δ yeast strains. Shown is the mean of three biological replicates (unpaired Student's t test; *, p < 0.05). Error bars, S.D. D, deletion of SNF2 affects steady-state levels of HA-tagged Ptc7 proteins. Proteins derived from the nonspliced and spliced forms of the PTC7-HA RNA are denoted as Ptc7nsHA and Ptc7sHA, respectively. Pgk1 (phosphoglycerate kinase 1) served as a loading control. E, serial dilutions (5-fold) of WT BY4741, snf2Δ, and coq2Δ (negative respiratory-deficient control; W303 background, because the deletion is unstable in the BY background) on YP agar plates with the indicated carbon sources.