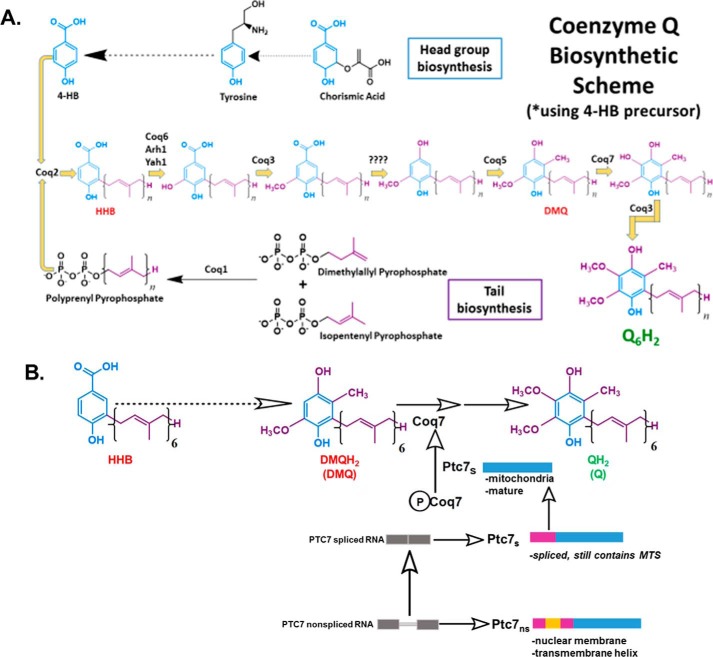
Figure 2.
CoQ6 biosynthetic pathway in S. cerevisiae and role of Ptc7s isoform on Coq7 phosphorylation and function. A, schematic of CoQ6 biosynthetic pathway in yeast using 4HB as a ring precursor, ultimately forming the reduced CoQ6H2 product in vivo. The question marks above the decarboxylation and second hydroxylation steps denote that the enzyme(s) responsible is still unknown. B, schematic of the CoQ6 biosynthetic pathway in yeast. The proposed function of Ptc7s as a mitochondrial phosphatase modulating Coq7 activity is indicated. Ptc7ns has been localized to nuclear membrane. The gray bars represent the exon regions of the RNA, and the thin gray line represents the intron region of the RNA. The pink-colored regions represent the predicted 38-amino acid mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) of the protein, the yellow region represents the 31-amino acid intron of the protein (which interrupts the MTS after amino acid 19, hence spanning from amino acid 20 to 50), and the blue region depicts the mature and spliced polypeptide, which spans from amino acid 51 to 374 (47).