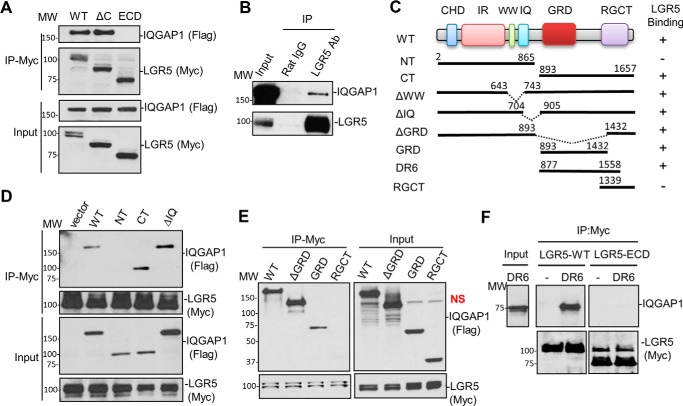
Figure 5.
LGR5 binds to the C-terminal half of IQGAP1. A, WB results of FLAG-tagged IQGAP1 co-IP with Myc-LGR5-WT, Myc-LGR5-ΔC, and membrane-tethered Myc-LGR5-ECD. B, WB results of co-IP of endogenous IQGAP1 and LGR5 in LoVo cells. C, a schematic diagram of IQGAP1 domain structure and the LGR5 binding results of various mutants tested. The domains are as follows: CHD, calponin homology domain; IR, IQGAP-specific repeat motif; WW, domain with two conserved Trp (W) residues; IQ, calmodulin-binding IQ motif; RGCT, RasGAP C terminus; NT, N terminus; CT, C terminus. The numbers denote the amino acid residues where mutant proteins/deletion regions start and end. D, WB results of co-IP of FLAG-IQGAP1 mutants with LGR5-WT using whole-cell lysates. E, WB results of co-IP of FLAG-IQGAP1 C-terminal tail mutants with Myc-LGR5-WT using whole-cell lysates. F, WB results of co-IP of purified IQGAP1 fragment (DR6; amino acids 877–1558) with LGR5-WT. NS, indicates nonspecific band. Each experiment was repeated two to three times, and shown here are representative WB results.