Figure 1.
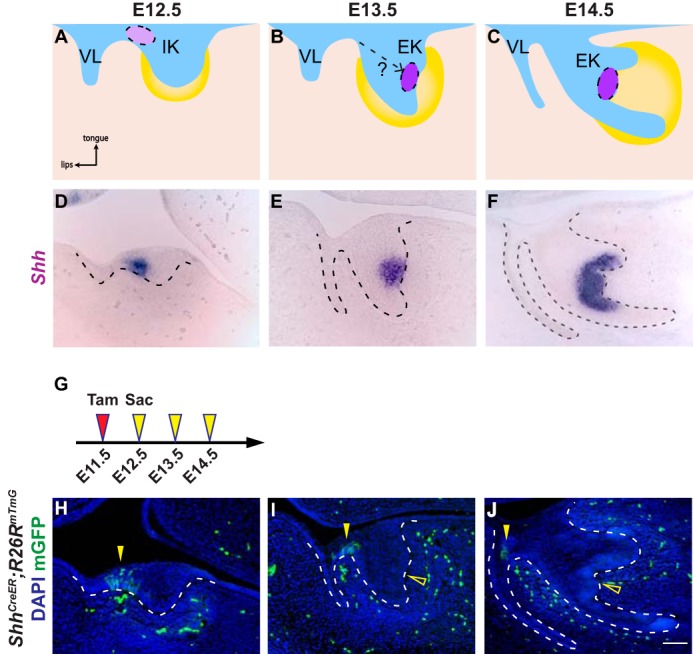
Incisor EK cells are not derived from the anterior IK population. A–C, schematic depiction of incisor development on sagittal sections. At E12.5, the dental epithelium (blue) invaginates into the underlying dental mesenchyme (yellow), forming a tooth bud. The initiation knot (light purple), which is the early signaling center of the incisor, is located at the anterior part of the incisor adjacent to the vestibular lamina (VL) (A). By E13.5, the tooth bud folds into a cap shape and the enamel knot (purple) forms (B). At E14.5, the incisor epithelium rotates posteriorly (C). D–F, in situ hybridization of Shh in the developing incisor tooth germ on sagittal sections from E12.5 to E14.5. G, timeline depicting the onset of Cre induction (Tamoxifen (Tam) injection, red arrowhead) and sample collection (yellow arrowheads). Tamoxifen concentration is 0.8 mg/30 g body weight. H–J, lineage tracing analysis of Shh-expressing cells in ShhCreER; R26RmTmG using 0.8 mg/30 g body weight of tamoxifen from E12.5 to E14.5. GFP-positive cells are only observed in the IK region (yellow arrowheads), but absent from the EK (open yellow arrowheads). n = 8 embryos for each time point. Scale bar in J represents 50 μm in D–F and H–J.
