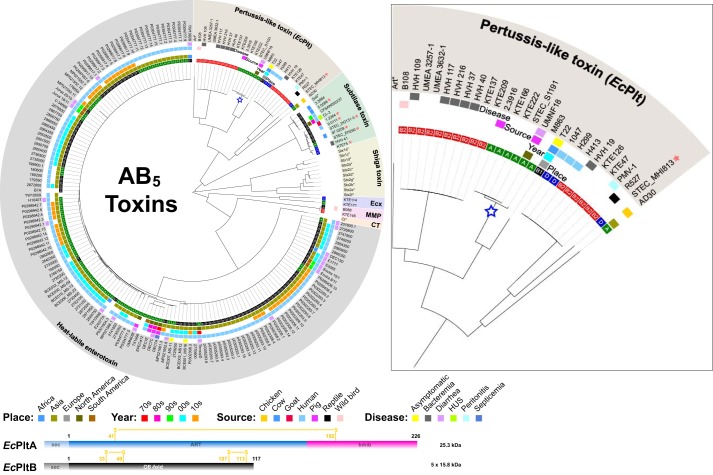
Figure 1.
E. coli AB5 toxins. Shown is a cladogram of AB5 toxin sequences identified in genome sequenced E. coli strains available on the NCBI database. Archetype sequences from the querying dataset are indicated with an asterisk. E. coli strains harboring more than one AB5 group are indicated by a red star. The inner circle represents the E. coli phylogenetic groups (A, B1, B2, and D). Additional color-coded circles indicate the place, year, and source of each strain, as well as the associated infection (where known). Because Shiga toxigenic E. coli strains are over-represented in the NCBI database, only archetypical Shiga toxin variants are presented. The EcPltA toxin focused on in this study is highlighted with a blue star. A schematic of the A and B subunit domain displayed with the positions of the intramolecular disulfides (yellow) and the inhibitory C terminus (pink) is at the bottom of the figure. Inset, an expanded view of the pertussis toxin branch. A complete overview of all Shiga toxin variants and their associated strains is presented in supplemental Fig. S1.