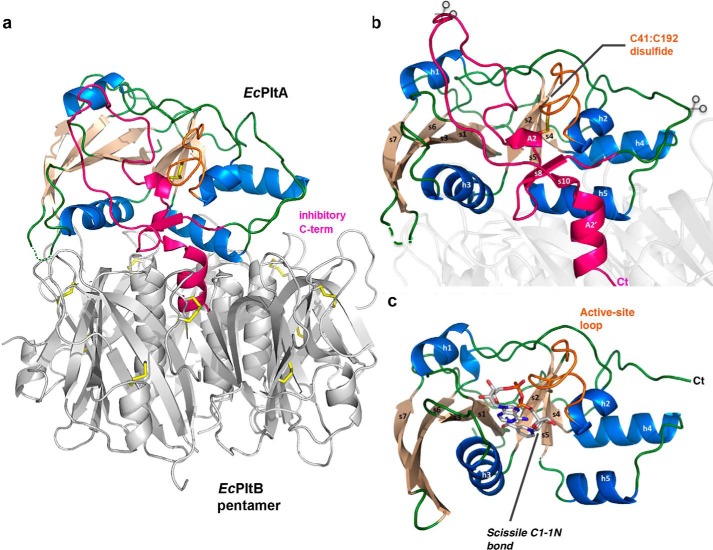
Figure 6.
Activation mechanisms of EcPlt and cholera toxin. a, schematic representation of the EcPltAB holotoxin in which α-helices are colored marine, β-strands wheat, and loop regions green. The C-terminal A2 domain is highlighted in pink showing its interaction with the B subunits of the glycan-binding pentamer (gray). b, schematic representation highlighting the holotoxin's EcPltA subunit. The conserved redox-sensing disulfide is labeled, and the rough position of the B-pentamer is shown as a partially transparent structure. Predicted potential proteolytic sites are shown with partially transparent scissors, and the C terminus is marked Ct. c, reduced active NAD+ co-complex with all secondary structural elements labeled. The enzymatically cleaved N-glycosidic bond cleaved during the course of the reaction is highlighted.