Figure 2. αKlotho administration attenuated cardiac remodeling after acute kidney injury (AKI).
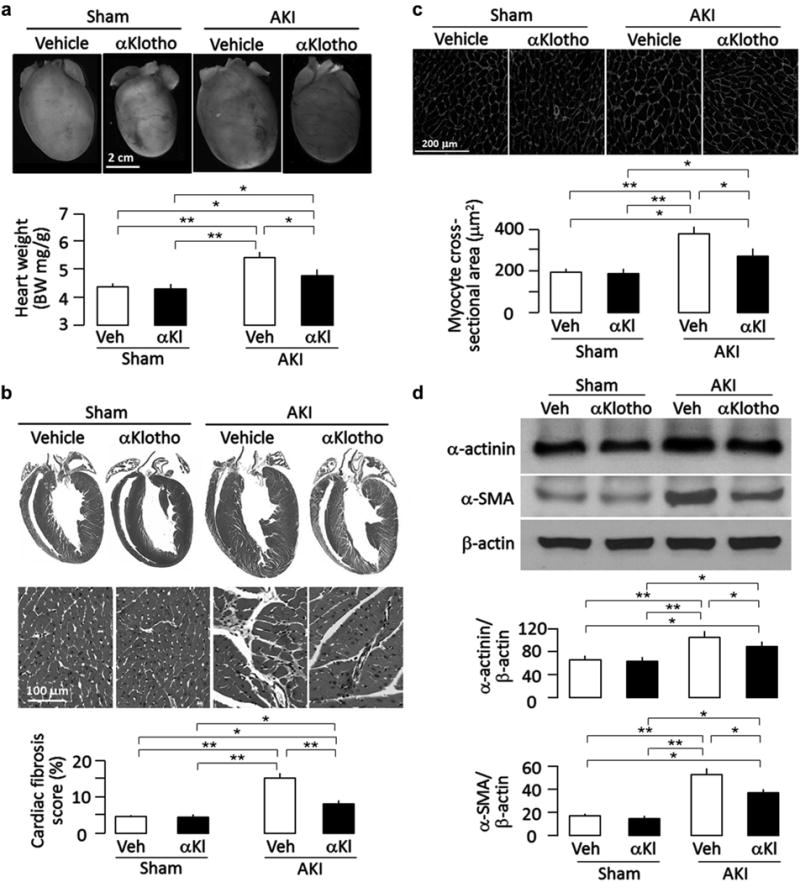
Wild-type mice subjected to ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI)–induced AKI and sham surgery were treated with αKlotho (αKl) protein (described in Supplementary Figure S1A) or vehicle (Veh) and killed 20 weeks after surgery. All mice were fed normal rodent chow, (a) Cardiac hypertrophy in mice after AKI. Upper panel shows representative gross macrographs of hearts. Bottom panel is a summary of ratio of heart weight to body weight of examined mice. (b) Cardiac fibrosis in mice after AKI. Upper panel shows representative macrographs of sagittal sections (trichrome stain). Middle panel shows representative micrographs of left ventricular sections (trichrome stain). Bottom panel is a summary of semiquantification of trichrome-positive area to whole heart section calculated using ImageJ software. (c) Hypertrophic cardiomyocytes in post-AKI mice. Upper panel shows representative micrographs of heart sections stained with WGA. Bottom panel is a summary of cardiomyocyte size calculated using ImageJ software, (d) Hypertrophic and fibrotic markers in the heart. Upper panel shows representative immunoblots for α-actinin, α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), and (β-actin protein. Bottom panel shows a summary of normalized protein quantification from all examined immunoblots. Data are expressed as means ± SD of 4 mice from each group, and statistical significance was assessed by 1-way analysis of variance followed by Student-Newman-Keuls test and accepted when: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 between 2 groups. WGA, wheat germ agglutinin.
